* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - Binghamton City School District
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
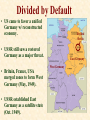
World War II The Impact of Total War Economic Damage: Western Europe Dresden After Allied Bombing • Impact of Strategic Bombing • 75% of Berlin Uninhabitable • 20 million homeless in Germany • Dutch lose 219,000 hectares of land • French lose 40% of prewar transportation systems • Norway lost 14% prewar capital The Human Cost 36½ million Europeans die! Deadliest and Most Destructive Conflict in Human History Military Deaths COUNTRY MILITARY DEATHS USSR 8.6 million D-Day Invasion Germany 4 million Italy 400,000 Rumania 300,000 COUNTRY Civilian Deaths USSR Poland Yugoslavia Greece France Hungary Netherlands Rumania ALL EUROPE CIVILIAN DEATHS 16 million 5 million 1.4 million 430,000 350,000 270,000 204,000 200,000 19 million Eastern Europe • Soviet troops physically occupied E. Europe at end of WWII. • USSR viewed E. Europe as essential to its security… It wanted a sphere of influence. Yalta (February, 1945) • U.S. & GB formally accept Soviet domination of Eastern Europe • Left out issue of Germany b/c it was so divisive • Did FDR sell out? The “Big Three” at Yalta Potsdam July 17-August 2, 1945 • Agreement to prosecute Axis war criminals (Nuremberg Trials) • Temporary division of Germany into 4 zones Atlee (GB) Truman • German question to be decided at final peace conference, which never occurs. Stalin (USA) (USSR) Divided by Default • US came to favor a unified Germany w/ reconstructed economy. Divided Berlin • USSR still saw a restored Germany as a major threat. • Britain, France, USA merged zones to form West Germany (May, 1949). • USSR established East Germany as a satellite state (Oct. 1949). East Germany West Germany The Nuremburg Trials (1946) • First known war crimes trial. • No clear legal precedent. • Most suspects claimed the court had no jurisdiction… Claimed it was “victor’s justice” • In all, about 1800 Germans tried after WWII • Similar trials were held in Japan & Italy The United Nations Truman Addresses the UN Conference (1945) • UN founded Oct. 1945 • Security Council – Five permanent members w/ vetoes: United States, Great Britain, France, USSR & China