* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
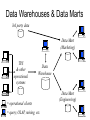
MP3 / MD740 Strategy & Information Systems Oct. 13, 2004 Databases & the Data Asset, Types of Information Systems, Artificial Intelligence Topics Covered • Data & Information • Data Warehousing • Leveraging Data – Harrah’s – Business Intelligence • Types of Information Systems – TPS, MIS, DSS • Artificial Intelligence – Expert Systems, Neural Networks, Genetic Algorithms Data, Information, & Knowledge • Data - raw facts, figures, and details. • Information - organized, meaningful, and useful interpretation of data. Has a context, answers a question. • Knowledge - an awareness and understanding of a set of information and how that information can be put to best use. • Many firms are data rich and info poor: victims of an old or poorly planned architecture Examples of Data, Information, & Knowledge Data: raw, no context 900,000 1,200,000 1,150,000 1,100,000 Information: meaningful, has context Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Post 900,000 1,150,000 Kellogg's 1,200,000 1,100,000 Knowledge: information above & other information creates an awareness of impact Post lowered its prices after the first quarter. Price change has caused Post sales to rise at the expense of Kellogg’s Warehouses & Marts • Data Warehouse – a database designed to support decision-making in an organization. It is structured for fast online queries and exploration. Data warehouses may aggregate enormous amounts of data from many different operational systems. • Data Mart – a database focused on addressing the concerns of a specific problem or business unit (e.g. Marketing, Engineering). Size doesn’t define data marts, but they tend to be smaller than data warehouses. Data Warehouses & Data Marts 3rd party data Data Mart (Marketing) TPS & other operational systems Data Warehouse = operational clients = query, OLAP, mining, etc. Data Mart (Engineering) Differing System Demands Operational Systems network traffic & processor demands time Managerial Systems network traffic & processor demands time “Let the neighbors lure tourists with knights on horseback, fiery volcanoes, pirate ships, and mini-Manhattans. We’ll just keep refining what we’re already pretty good at: drilling into our data and making sure our regular customers are more than satisfied.” - Gary Loveman, CEO, Harrah’s Types/Classifications of Information Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) • A shared IS that uses a combination of IT and manual procedures to process data and information and to manage transactions. • Examples: Cash Registers (POS), ATM • Characteristics: – transactions are similar & repeatable – support multiple users in routine, everyday transactions (usually tactical systems) – data capture with possible report generation – accuracy is critical, TPS “feed” other IS Reporting Systems - MIS • Sometimes called Management Reporting Systems or Management Information Systems • Characteristics – use data captured and stored from TPS – reports consolidated information rather than details of transactions – supports reoccurring decisions – provides reports in pre-specified formats (on screen, printed, or data) Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Allow users interrogate computers on an ad hoc basis, analyze information, and predict the impact of decisions before they are made. [key: unstructured, user-led exploration] • Characteristics – Assists in ad-hoc decision making – Used when requirements, processes, or procedures are unstructured & aren’t known in advance – Provides info needed to define & solve a problem – Provides information in format determined at time of need Management Levels & IS Strategic Planning Management Control Operational Control DSS MIS TPS Expert Systems (ES) • An artificial intelligence system that uses captured human expertise to evaluate and solve problems • Characteristics: – diagnosis, configuration, and/or recommend a course of action – problems are structured and repeatable – application scope is limited to a particular problem area (domain) Other Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI) • Neural Networks – hunt for patterns in historical data – build their own expertise based on prior history – require clean data & consistency between performance history and future events • Genetic Algorithms – search for optimal solutions based on natural selection: (1) propose solution (2) evaluate results against earlier solution (3) mutate & return to step 1 Keane’s Space Truss Design