* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Managing Knowledge
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
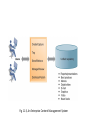
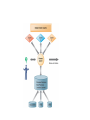
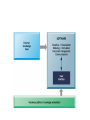
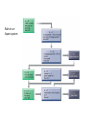
Managing Knowledge Making organizational knowledge more Accessible, Quality, & Currency • Canadian Tire – Five interrelated companies • 57,000 employees • 1,200 stores – Independently owned and operated – Spread across Canada – Need efficient and effective ways to communicate with workforce and dealers – Dealer portal & employee information intranet – Dealer portal • Central source for – – – – – Merchandise setup info Alerts Best practices Products ordering Problem solution • Save money by reducing daily and weekly mailings • Easy access info for dealers – Employee intranet • • • • TIREnet Catalogued more than 30,000 documents Search technology Easier to keep document current – Reduce the time required to find info 11.1 The knowledge management landscape 11.2 Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems 11.3 Knowledge work systems 11.4 Intelligent techniques • The knowledge management landscape – Communicating & sharing knowledge • Knowledge management • Collaboration – Production & distribution • Information • Knowledge – Companies’ value depend on • its ability to create and manage knowledge • Important dimensions of knowledge – Data • Events or transactions captured – Information • Organized data into categories of understanding – Monthly, regional, store-based reports – Knowledge • Discover patterns, rules, and contexts where the knowledge works – Wisdom • Collective and individual experience of applying knowledge – Where, When, How – Tacit knowledge • Knowledge resides in the mind of employees – Explicit knowledge • Knowledge has been documented – Emails – Voice mails – Graphics – Knowledge is • Situational & contextual – Organizational learning and Knowledge management • The ability to reflect and adjust from learning – Create new business process – Change of patterns of management decision • The knowledge management value chain • Knowledge acquisition – Corporate repositories • Documents, reports, presentations, best practices • Unstructured documents – Online expert networks • Enable employee to find “experts” – Knowledge work stations • Discovering patterns in corporate data • Knowledge storage – System for employees to retrieve and use knowledge – Encourage the development of corporate-wide schemas for indexing documents – Reward employees for taking time to update and store documents properly • Knowledge Dissemination – Portal – Email – Instant message – Wikis – Social networks – Search engines – Collaboration technologies • Knowledge application – Build knowledge into • • • • Decision makings systems Decision support systems Business processes Enterprise systems – ERP – SCM – CRM • Building organizational and management capital: Collaboration, community of practice, & office environments – Communities of Practice • Professionals and employees – Similar work-related activities and interests • Reduce the learning curve for new employees • Spawning ground for new ideas • Types of knowledge management systems 11.1 The knowledge management landscape 11.2 Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems 11.3 Knowledge work systems 11.4 Intelligent techniques – Three kinds of knowledge • Structured text documents – Reports, presentations • Semi-structured – Emails, digital pictures, graphs • Tacit knowledge – Reside in the heads of employees • Enterprise content management systems – Capabilities for knowledge • • • • • Capture Storage Retrieval Distribution Preservation – Enable users to access external sources of info – Create a portal for easy access Fig 11-3, An Enterprise Content Management System – Leading vendors • • • • Open Text Corporation EMC (Documentum) IBM Oracle • Taxonomy – Classification scheme – Organize information into meaningful categories • Knowledge network systems – Expertise location and management systems – Online directory of corporate experts – Best practices knowledge base – FAQ repository • Collaboration tools and Learning management systems – Web technology to foster collaboration and information exchanges • • • • Portal Emails Chat, instant message Blog, wikis – Social bookmarking • • • • Users save their bookmarks Tag bookmarks Tags can be shared or searched Delicious, Digg – Learning management systems • Track and manage employee’s learning • Whirlpool corporation – Training program for 3,500 salepeople 11.1 The knowledge management landscape 11.2 Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems 11.3 Knowledge work systems 11.4 Intelligent techniques • Specialized systems for knowledge worker to create new knowledge • Knowledge workers – Researchers – Designers – Architects – Scientists – Engineers • Requirements of knowledge work systems – Substantial computing power for graphics, complex calculations – Powerful graphics and analytical tools – Communications and document management – Access to external databases – User-friendly interfaces – Optimized for tasks to be performed (design engineering, financial analysis) • Examples of knowledge work systems – Computer-aided design (CAD) • Traditional – A Mold – A Prototype • CAD – Designs can be easily tested and changed – Virtual reality systems • Boeing CO. • 787 Dreamliner mechanics’ training – Augmented reality • Enhance a direct or indirect view of a physical realworld environment – Virtual reality for the web • Virtual reality modeling language • DuPont Chemical – VRML for a virtual walkthrough of a plant 11.1 The knowledge management landscape 11.2 Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems 11.3 Knowledge work systems 11.4 Intelligent techniques • Tools to capture individual and collective knowledge – Capture tacit knowledge • Expert systems • Case-based reasoning • Fuzzy logic – Discovering knowledge • Neural networks • Data mining – Generating solutions to problems • Genetic algorithm – Automate routine tasks • Intelligent agent – Artificial intelligence (AI) • To emulate human behavior Watson Won Jeopardy • Capturing knowledge: expert systems – Specific and limited domain of human expertise – Compare to human experts, ES lack • the breadth of knowledge • the understanding of fundamental principles – Diagnosis a m/c – Grant credit of a loan Rules in an Expert system – Knowledge base • 200 to many thousands of rules – Inference engine • Forward chaining – Begin with the info entered by the users – Search the rule base – Arrive a solution • Backward chaining – Start with a hypothesis – Asking the user questions – Until hypothesis is confirmed or disproved – Examples of successful expert systems • Con-Way transportation • Automate and optimized planning of overnight shipping route – 50,000 shipments of heavy freight each night – across 25 states • Dispatcher tweak the routing plan provide by the expert system • Organizational intelligence: case-based reasoning – Cases • Descriptions of past experiences of human specialists – Systems • Search the stored cases – Find the closest fit and applied the solution EX: diagnostic systems in medicine • Fuzzy logic systems – Human • tend to categorize things imprecisely – Each categories represent a range of values • Use rules for making decisions that may have many shades of meaning • Applications – Sendai subway system • Use fuzzy logic control to accelerate • so smoothly that standing passengers need not hold on. – Auto focus of cameras • Neural network – Solving complex, poorly understood problems – Large amount of data have been collected – Parallel the processing patterns of the biological or human brain – Learn the correct solution by examples • Applications – Screening patients for disease – Visa international • Detect credit card fraud • Genetic algorithm – Finding the optimal solution for a specific problem • Dynamic and complex – Involve hundreds or thousands of variables or formulas • Large number of possible solutions exists – Inspired by evolutionary biology • Inheritance, mutation, selection, crossover (recombination) – Examples • GE Jet Turbine Aircraft Engine – Each design change requires changes in up to 100 variables • i2 technology – Supply chain management software – Optimize production-scheduling models » Customer orders » Material » Manufacturing capability » Delivery dates … • Hybrid AI systems – Neurofuzzy washing machines • Intelligent agent – Software programs that work in the background • Without human intervention • To carry out specific, repetitive, and predictable tasks INTELLIGENT AGENTS IN P&G’S SUPPLY CHAIN NETWORK Interactive session (Minicase) – 技術 • 擴增實境:真實世界變得更美好 • 頁 488 – 組織 • 資訊科技使 Albassami 的工作成為可行 • 頁 500