* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How do organisms obtain energy?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
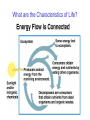
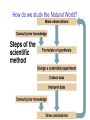
Everyone is a Biologist ! Today: Four Questions What are the Characteristics of Life? How diverse is life? How do we study the natural world? Who are some of the key people who played a role in the history of biology? What are the Characteristics of Life? All living things exhibit five characteristics in combination. What are the Characteristics of Life? What are the Characteristics of Life? MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM ORGAN SYSTEM ORGAN TISSUE CELL ORGANELLE MOLECULE ATOM What are the Characteristics of Life? What are the Characteristics of Life? Each level of biological organization exhibits emergent properties. Ex. Capillaries transport blood (property not exhibited by individual endothelial cells). What are the Characteristics of Life? Energy Use & Metabolism Metabolism - biochemical reactions that acquire & use energy. Why do organisms need energy? How do organisms obtain energy? What are the Characteristics of Life? What are the Characteristics of Life? Maintenance of Homeostasis Homeostasis - the ability of an organism to maintain its internal environment despite conditions in the external environment. Human body temperature is……… if body temperature rises, you sweat. if body temperature lowers, you shiver. What are the Characteristics of Life? Reproduction, Growth & Development Asexual reproduction - involves a single parent; progeny are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction - involves 2 parents; progeny are genetically diverse. Is it essential for an individual to reproduce? What are the Characteristics of Life? Irritability & Adaptation Irritability - immediate response to a stimulus. What are the Characteristics of Life? Irritability & Adaptation Adaptation - an inherited behavior or characteristic that enables an organism to survive & reproduce. Over time, adaptations are modified by natural selection. What are the Characteristics of Life? Life is always changing….. On the level of DNA…… Change = Evolution Evolution is the backbone of biology. Life is Diverse Biodiversity refers to the many different types of organisms on earth. Taxonomy is the biological science that classifies life according to evolutionary relationships. The Domain is the largest group of organisms. Life is Diverse Life is Diverse Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Kings Play Chess On Funny Green Squares Life is Diverse Human classification scheme: Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus & species Eukarya Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Homo sapiens How do we study the Natural World? What is the Scientific Method? Methodical exploration What makes science unique! How do we study the Natural World? Observations Question Hypothesis Prediction Now What??? How do we study the Natural World? Observations Question Hypothesis Prediction Experiment How do we study the Natural World? How do we study the Natural World? After you perform your experiment, you need to analyze the generated data. Does the data support or not support your hypothesis? If your data does not support the hypothesis then…… If your data does support your hypothesis…….. How do we study the Natural World? What is difference between hypothesis, theory & law? Hypothesis - “an educated guess”; a tentative explanation of phenomena. Theory - a widely accepted explanation of natural phenomena; has stood up to thorough & continual testing. Law - a statement of what always occurs under certain conditions. How do we study the Natural World? How is a control group different from an experimental group? History of Biology Aristotle (384-322BC) Began much of what we call biology today Microbiology Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) Father of Microbiology Best known for his work on the improvement of the microscope and for his contributions towards the establishment of microbiology Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) Great biologist in numerous areas Cell Biology Robert Hooke (1635-1703) Coined the biological term “cell” Cell Theory Theodore Schwann (1810-1882) Co-founder of the cell theory Stated that the different parts of animals are composed of cells Matthias Jakob Schleiden (1804-1881) Co-founder of the cell theory Stated that the different parts of plants are composed of cells Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) Supplied the third part of the cell theory stating that every cell originates from another cell Genetics Gregor Johann Mendel (1823-1884) Father of Genetics Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Father of Evolution by Natural Selection DNA James Watson (1928- ) and Francis Crick (1916-2004) Discovered the structure of DNA in 1953 Rosalind Franklin (1920-1958) Helped Watson & Crick significantly with the discovery of the structure of DNA DNA Martha Chase (1923-2003) and Alfred Hershey (1908-1997) Provided more evidence that DNA, not protein, was the genetic material in 1953 Oswald Avery (1877–1955) Discovered that DNA is the material of which genes and chromosomes are made