* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 18.2 Telescopes
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
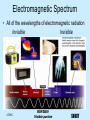
Chapter 18.2 Telescopes Invention of the Telescope Telescopes • Definition An instrument that gathers electromagnetic radiation from objects in space and concentrates it for better observation. Optical Telescopes • The most common type of telescope. • Collects and focuses visible light for closer observation. • Focal Point: – Point where the rays of light converge in the telescope. • Simplest Telescope has two lenses: – Objective lens- collects light and forms image at the back of telescope – Eyepiece lens- magnifies the image Refracting Telescope • Definition: – Uses a set of lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects • Disadvantages: – Cannot focus images perfectly because lenses focus different colors at different distances – Distorts images if lenses are too large because the glass sags under its own weight Refracting Telescopes http://encarta.msn.com/media_461518089_1741502444_-1_1/Refracting_Telescope.html Reflecting Telescope • Definition: – Uses a curved mirror to gather and focus light from distant objects • Used by most professional astronomers b/c: – Mirrors can be very large (gather more light) – Mirrors are polished (flaws don’t affect light) – All colors of light focus to same point (all colors seen in focus at same time) Reflecting Telescope Reflecting telescopes use curved mirrors instead of convex lenses to collect and focus light. A large concave mirror (the center is thinner than the edges) collects and reflects the light to make an image. Once the image forms, the lens in the eyepiece magnifies the image. Reflecting telescopes are very helpful for viewing dim or dark objects. Large reflecting telescopes can see objects that are a millionth or a billionth the brightness of the faintest star that can be seen by the human eye alone! http://library.thinkquest.org/J0112188/refracting_and_reflecting_telescopes.htm How Telescopes Work The Atmosphere • “Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star” • Stars don’t “twinkle”- the atmosphere causes starlight to shimmer and blur and look like it’s twinkling • Light gathered by telescopes on the Earth’s surface is affected by the atmosphere • On Earth- top of mountain is good location for telescope because of thinner air • Best place- Space because no atmosphere to interfere with light Electromagnetic Spectrum • All of the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation Invisible Invisible LONG ROYGBIV Visible portion SHORT Electromagnetic Radiation Nonoptical Telescopes • Detect radiation that is not visible. • Example- Radio Telescope is much larger because radio wavelengths are longer. • Many nonoptical telescopes are put in space because wavelengths are blocked by atmosphere. The Lovell Radio Telescope. http://www.nmm.ac.uk/server/show/conWebDoc.411 The Hubble Telescope • Read p. 558 – 563 • Questions p. 563 (in your notebook) • Show me your answers when finished, so I can put them in the gradebook.