* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light - SCHOOLinSITES
Holiday lighting technology wikipedia , lookup
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
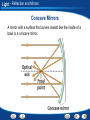
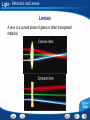
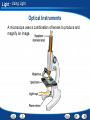
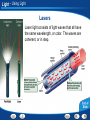
Light Table of Contents Light and Color Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and Lenses Seeing Light Using Light Light - Light and Color When Light Strikes an Object When light strikes an object, the light can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Light - Light and Color The Color of Objects The color of an opaque object is the color of the light it reflects. Light - Light and Color The Color of Objects The color of a transparent or translucent object is the color of the light it transmits. Light - Light and Color Combining Colors As pigments are added together, fewer colors of light are reflected and more are absorbed. Light - Light and Color Building Vocabulary Using a word in a sentence helps you think about how best to explain the word. After you read the section, carefully note the definition of each Key Term. Also note other details in the paragraph that contain the definition. Use all this information to write a sentence for each Key Term. Key Terms: transparent primary colors material translucentcolor secondary material opaque materialcolors complementary pigment Examples: Three A transparent colors that material can combine transmits to make most any of the other lightcolor that strikes are called it. primary colors. A translucent Two primary colors material combine scatters in equal light amounts as it passes to through. a secondary color. produce An opaque Any two colors material that combine reflects to or form absorbs white alllight of the arelight that strikes called complementary it. colors. Pigments are colored substances that are used to color other materials. Light - Light and Color Color Click the Video button to watch a movie about color. Light - Light and Color Links on Colors Click the SciLinks button for links on colors. Light End of Section: Light and Color Light - Reflection and Mirrors Reflection of Light Rays The two ways in which a surface can reflect light are regular reflection and diffuse reflection. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Concave Mirrors A mirror with a surface that curves inward like the inside of a bowl is a concave mirror. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Concave Mirrors Ray diagrams show where an image forms and the size of the image. The steps below show how to draw a ray diagram. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Concave Mirrors Concave mirrors can form either virtual images or real images. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Convex Mirrors A mirror with a surface that curves outward is called a convex mirror. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Mirrors Activity Click the Active Art button to open a browser window and access Active Art about mirrors. Light - Reflection and Mirrors Comparing and Contrasting As you read, compare and contrast concave and convex mirrors in a Venn diagram like the one below. Write the similarities in the space where the circles overlap and the differences on the left and right sides. Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Real images Enlarged images Curves inward Virtual images Reduced images Curves outward Light End of Section: Reflection and Mirrors Light - Refraction and Lenses Bending Light The index of refraction of a medium is a measure of how much light bends as it travels from air into the medium. The table shows the index of refraction of some common mediums. Light - Refraction and Lenses Bending Light Interpreting Data: Which medium causes the greatest change in the direction of a light ray? Diamond causes the greatest change in the direction of a light ray traveling from air. Light - Refraction and Lenses Bending Light Interpreting Data: According to the table, which tends to bend light more: solids or liquids? According to the graph, most solids bend light more than liquids do (quartz is an exception). Light - Refraction and Lenses Bending Light Predicting: Would you expect light to bend if it entered corn oil at an angle after traveling through glycerol? Explain. You would not expect light to bend if it entered corn oil at an angle after traveling through glycerol, because corn oil and glycerol have the same value for the index of refraction. Light - Refraction and Lenses Refraction of Light When light rays enter a medium at an angle, the change in speed causes the rays to bend or change direction. Light - Refraction and Lenses Lenses A lens is a curved piece of glass or other transparent material. Light - Refraction and Lenses Lenses An object’s position relative to the focal point determines whether a convex lens forms a real image or a virtual image. Light - Refraction and Lenses Lenses A concave lens can produce only virtual images because parallel light rays passing through the lens never meet. Light - Refraction and Lenses Lenses Activity Click the Active Art button to open a browser window and access Active Art about lenses. Light - Refraction and Lenses Asking Questions Before you read, preview the red headings. In a graphic organizer like the one below, ask a what, when, where, or how question for each heading. As you read, write answers to your questions. Question Answer When does refraction occur? When light rays enter a medium at an angle What are the types of lenses? Concave and convex lenses Light End of Section: Refraction and Lenses Light - Seeing Light Correcting Vision Concave lenses are used to correct nearsightedness. Convex lenses are used to correct farsightedness. Light - Seeing Light Sequencing Sequence is the order in which the steps in a process occur. As you read, make a flowchart that shows how you see objects. Put the steps of the process in separate boxes in the order in which they occur. How You See Objects Light enters the eye. Light focuses on the retina. An image forms. Rods and cones send signals to the brain. Light - Seeing Light More on Eyesight Click the PHSchool.com button for an activity about eyesight. Light End of Section: Seeing Light Light - Using Light Optical Instruments A telescope forms enlarged images of distant objects. Telescopes use lenses or mirrors to collect and focus light from distant objects. Light - Using Light Optical Instruments A microscope uses a combination of lenses to produce and magnify an image. Light - Using Light Optical Instruments The lens of the camera focuses light to form a real, upsidedown image on film in the back of the camera. Light - Using Light Lasers Laser light consists of light waves that all have the same wavelength, or color. The waves are coherent, or in step. Light - Using Light Optical Fibers The floodlight in the swimming pool gives off light rays that travel to the surface. If the angle of incidence is great enough, a light ray is completely reflected back into the water. This complete reflection of light by the inside surface of a medium is called total internal reflection. Light - Using Light Optical Fibers Optical fibers can carry a laser beam for long distances because the beam stays totally inside the fiber as it travels. Light - Using Light Building Vocabulary A definition states the meaning of a word or phrase by telling about its most important feature or function. Carefully read the definition of each Key Term. Then write a definition of each Key Term in your own words. Key Terms: Examples: microscope total internal reflection telescope The A microscope total internal is device an reflection instrument is the that complete formsorenlarged reflection telescope is a that uses lenses mirrors to images of light and by of the tiny inside objects usingdistant lenses. of a medium. collect focus lightsurface from objects. camera refracting telescope A camera is atelescope device that lenses that to focus refracting is uses a telescope useslight on film to record convex lensesan toimage. focus light. A is a device produces intense beam of Anlaser objective is thethat large lens in aan telescope or coherent light. microscope that gathers and focuses light. A three-dimensional photograph Anhologram eyepiece isisathe lens near the eye in a telescope or created by athat laser. microscope magnifies the image. An optical fiber is a strand glass orthat plastic that A reflecting telescope is a of telescope uses a can carry lightmirror long distances. concave to gather light. laser objective hologram eyepiece optical fiber reflecting telescope Light - Using Light Links on Lasers Click the SciLinks button for links on lasers. Light End of Section: Using Light Light Graphic Organizer Type of Mirror Effect on Light Rays Type of Image Plane Regular reflection Virtual Concave Converge Real or virtual Convex Spread out Virtual Type of lens Effect on Light Rays Type of Image Convex Converge Real or virtual Concave Spread out Virtual Light End of Section: Graphic Organizer