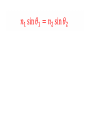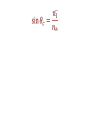* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics_AP_B_Evans_Day_36_Period_2
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
AP Physics IV.C Geometric Optics Wave Fronts and Rays IV.C.1 Reflection of Light Specular and diffuse reflection IV.C.2 Plane Mirrors Five Properties of the image of a Plane Mirror • Upright • Same size • Located as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror • Left to right reversed • Virtual image Ray Diagram for a Plane Mirror Ex. What is the minimum mirror height needed for a person to see their full image? Spherical Mirrors (concave – converging and convex – diverging) The focal length and radius of curvature Ray diagrams for curved mirrors. Only two rays are needed to locate an image • Any ray drawn parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the focal point • Any ray drawn through the focal point is reflected parallel to the principal axis • Any ray incident upon the mirror is reflected at the same angle when measured from the normal • Any ray drawn through the center of curvature is reflected upon itself The mirror equation and magnification (and an impressive proof thrown in for free) Summary of sign conventions for curved mirrors • f is positive for a concave mirror and negative for a convex mirror • so is positive for an image located in front of the mirror (our only concern at this point) • si is positive for a real image (in front of the mirror) and negative for a virtual image (behind the mirror) Ex. A 2.00 cm object is placed 7.10 cm from a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 10.20 cm. Find the location and size of the image. Ex. An object with a height of 1.20 cm is placed 6.00 cm in front of a concave mirror with a focal length of 10.0 cm. Find the location and height of the image. Ex. An object is placed 66 cm in front of a convex mirror that has a focal length of 46 cm. Find the image distance and magnification. IV.C.3 Refraction and Lenses Refraction – the bending of light as it passes between two media with different optical densities Snell’s Law Ex. Light is incident upon an equilateral crown glass prism at an angle of 45.0º to one face. Calculate the angle at which the light emerges from the opposite face. Total Internal Reflection Ex. A ray of light in a diamond (n = 2.42) strikes an interface at 28º. Will the beam of light enter the air or will it be reflected internally? Will the beam of light be reflected internally if the diamond is surrounded by water? Applications of total internal reflection Dispersion of Light Lenses Two types of lenses Images formed by converging lenses Image formed by a diverging lens A familiar friend Sign conventions for lenses: • f is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses • so is positive when light is reflected from the object (a real object) • si is positive when it is behind the lens (real image) and negative when it is in front of the lens (virtual image)