* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TELESCOPE08
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
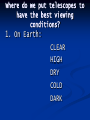
TELESCOPES Where do we put telescopes to have the best viewing conditions? 1. On Earth: CLEAR HIGH DRY COLD DARK Problem with Telescopes on Earth? Problem: Particles of all sorts in the atmosphere block and cloud the view 2. In Space Solves atmosphere problem – CLEAR VIEW! Examples: Hubble, Cobe , Iras Problem with telescopes in space? They’re in space! Hard to get to Hard to repair EXPENSIVE!!! Functions of a Telescope 1. 2. 3. 4. Collect Light Magnify Images Separate Distant Objects Use as a Camera OPTICAL TELESCOPES (USE VISIBLE LIGHT) Two types: 1. Refractor – BENDS LIGHT Invented by Hans Lippershey in 1608 Refined by Galileo in 1609 Galileo demonstrating his telescope 2. Reflector – USES MIRRORS Tololo Observatory - Chile TYPE 1 – REFRACTING TELESCOPE How does it work? a. b. It bends light to create an image It uses two lenses 1. eyepiece (ocular) lens - small 2. objective lens - large Draw it! Type 2 – Reflecting Telescope a. b. c. Invented by Isaac Newton in 1668 Uses two mirrors Objective Mirror – Large Secondary (flat) mirror – Small Can be VERY LARGE 40 ft - 50 ft diameter objective mirror! Draw It! Advantages of a reflector 1. 2. You only need to prepare one side of the mirror. (on a refractor the lens has two sides) – cheaper and distortion is less of a problem. The whole back of the mirror can be supported, therefore can be made very LARGE Non-optical Telescopes 1. Radio Telescopes a. Location – Earth (atmosphere does not affect radio waves) b. Structure – Large metal dish c. Size – very large because radio waves have a very long wavelength d. Arrays – sets of multiple radio telescopes that allow for more data to be gathered. Ex – VLA (very large array) in Socorro, New Mexico 27 dishes. SETI– Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence looking for intelligent radio signals Other Non-Optical Telescopes (all are satellites) a. Infrared – IRAS launched 1983 b. Microwaves – COBE Cosmic Background explorer. Discovered evidence of the Big Bang. Launched 1981 COBE Image of CBR c. X-Rays – Chandra Launched 1999 Cassiopeia Super Nova Black Hole Crab Nebula Saturn d. Gamma Rays – GRO Gamma Ray Observatory Milky Way