* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Optical rectenna wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
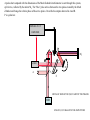
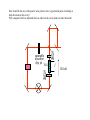
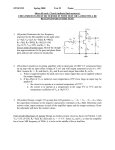
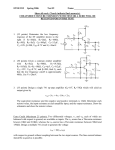
In the optical sytem sketched here, linearly polarized light from an oscillator goes through an “optical isolator” consisting in a combination of polarizing cubes, a (45 deg) Faraday rotator, and a wave plate. The beam goes through a series of optical systems (stretcher, regenerative amplifier) before being sent to the multipass amplifier. These optical systems return the same polarization. Indicate by a sketch (xin the plane of the figure, y orthogonal, and z along k) the state of polarization at each passage through a polarizing element. Explain why (how) the beam can be made to follow the red arrows. Regenerative Amplifier Temporal Compressor Multipass Power Amplifier Temporal Stretcher To Frequency Tripler l/2 From Ti:Sapphire Oscillator Optical Isolator p-polarized The regenerative amplifier. The s-polarized beam (pulse train) comes from the isolator (arrives from the top of this figure), is deflected by a thin film polarizer TFP. What is the voltage sequence to be applied to the Pockel’s cell PC such that at t<0 all pulses make a single passage through the cavity before being extracted. At t=0 one pulse is trapped in the cavity until it makes 20 RT, and is extracted at t = te s-polarized Express all voltages as fraction of the half wave voltage Vhw TS FM p-polarized Pump Beam EM2 PM TFP PC=Pockel Cell; PM= Pump Mirror; TFP=Thin Film Polarizer; FM= Folding Mirror; TS= Ti:Sapphire Crystal; EM1= End Mirror (R=3m); Em2= End Mirror (Flat) PC A pulse short compared with the dimensions of the Mach Zehnder interferometer is sent through this system, split in two, reflected by the mirror M2. The “blue” pulse arrives between the two pulses created by the Mach Zehnder and change the relative phase of these two pulses. Describe the outputs detected in A and B. P is a polarizer. TRIPLER -FS UV AMPLIFIER M2 l/2 LASER M A P E B METALLIC REFLECTOR (M) TO ADJUST THE PHASES CCD ETALON (E) TO BALANCE THE AMPLITUDES Explain the path and polarization of the pulse circulating clockwise and counterclockwise in the ring and in the tail of the ring. How should be the axis of the quarter wave plates to have a p polarized pulse circulating in both directions in this cavity? Will a magnetic field (as indicated) have an effect on the cavity modes in either direction? saturable absorber dye jet TGG l B field