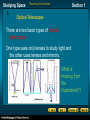
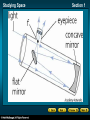
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download telescope
Survey
Document related concepts
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Studying Space Section 1: Viewing the Universe Preview • Key Ideas • The Value of Astronomy • Characteristics of the Universe • Observing Space • Telescopes • Space-Based Astronomy Section 1 Studying Space Section 1 Key Ideas • Describe characteristics of the universe in terms of time, distance, and organization. • Identify the visible and nonvisible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. • Compare refracting telescopes and reflecting telescopes. • Explain how telescopes for nonvisible electromagnetic radiation differ from light telescopes. Studying Space Section 1 The Value of Astronomy • Astronomy: the scientific study of the universe (Observation) • Scientists who study the universe are called astronomers. • In the process of observing the universe, astronomers have made exciting discoveries, such as new planets, stars, black holes, and nebulas. • By studying these objects, astronomers have been able to learn more about the origin of Earth and the processes involved in the formation of our solar system. Studying Space Section 1 The Value of Astronomy, continued • Astronomy & Cosmology are extremely similar in nature. Here is the distinction: • Astronomy is the act of observation and discovery through observation. • Cosmology: is to understand broader questions about the Universe, such as its origin, underlying physical laws etc. Cosmology requires astronomy and astrophysics in order to get data to compare to cosmological models Studying Space Section 1 Characteristics of the Universe, continued Measuring Distances in the Universe • astronomical unit the average distance between the Earth and the sun; approximately 150 million kilometers (symbol, AU) • Astronomers also use the speed of light to measure distance. • Light travels at 300,000 km/s. In one year, light travels 9.46 x 1012 km. This distance is known as a light-year. • Aside from the sun, the closest star to Earth is 4.22 light-years away. Studying Space Section 1 Observing Space Electromagnetic Spectrum • electromagnetic spectrum all of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. • Light, radio waves, and X rays are all examples of electromagnetic radiation. • Electromagnetic radiation is composed of traveling waves of electric and magnetic fields that have fixed wavelengths and therefore fixed frequencies. Studying Space Section 1 Observing Space, continued Visible Electromagnetic Radiation • The human eye can see only radiation of wavelengths in the visible light range of the spectrum. • The shortest visible wavelength of light are blue and violet, while the longest visible wavelength of light are red. • Electromagnetic radiation shorter than wavelengths of violet or longer than wavelengths of red light cannot be seen by humans. • These invisible wavelengths include infrared waves, microwaves, radio waves (at longer wavelengths than red), as well as ultraviolet waves, X rays, and gamma rays (at shorter wavelengths than blue). Studying Space Section 1 Reading check Which type of electromagnetic radiation can be seen by humans? The only kind of electromagnetic radiation the human eye can detect is visible light. Studying Space Section 1 Observing Space, continued Invisible Electromagnetic Radiation • In 1800, the scientist William Herschel discovered infrared, which means “below the red.” • Infrared is electromagnetic radiation that has waves longer than those of visible light. • The ultraviolet wavelengths, which are invisible to humans, are shorter than the wavelengths of violet light. • Ultraviolet means “beyond the violet.” • The X-ray wavelengths are shorter than the ultraviolet wavelengths. The shortest wavelengths are the gammaray wavelengths and the longest are radio waves. Studying Space Section 1 Telescopes • In 1609, an Italian scientist, Galileo, built a device that used two lenses to make distant objects appear closer and turned it toward the sky. • telescope an instrument that collects electromagnetic radiation from the sky and concentrates it for better observation • optical telescopes : Telescopes that collect only visible light . • The two types of optical telescopes are refracting telescopes and reflecting telescopes. Studying Space 1 Observing the Universe Section 1 Optical Telescopes There are two basic types of optical telescopes. One type uses only lenses to study light and the other uses lenses and mirrors. What is missing from the illustratons?? Studying Space 1 Observing the Universe Section 1 Optical Telescopes You can find the magnifying power (Mp) of a telescope by dividing the focal length of the objective (fo) by the focal length of the eyepiece (fe). Studying Space Section 1 1 – What is the difference between astronomy & cosmology 2 – An optical telescope can only see in the visible light range – T or F 3 – Name the 2 types of Optical telescopes 4 – Is light a form of electromagnetic energy? Studying Space Section 1 Telescopes, continued Refracting Telescopes • refracting telescope a telescope that uses a set of lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects • The bending of light is called refraction. • Refracting telescopes have an objective lens(big one) and an eyepiece(small one). • One problem with refracting telescopes is that the lens focuses different colors of light at different distances causing the image to distort. • It is difficult to make very large lenses because they sag distorting the image. Studying Space Section 1 Telescopes, continued Reflecting Telescopes • reflecting telescopes a telescope that uses a curved mirror to gather and focus light from distant objects • When light enters a reflecting telescope, the light is reflected by a large curved mirror to a second mirror. The second mirror reflects the light to the eyepiece, where the image is magnified and focused. • Mirrors in reflecting telescopes can be made very large without affecting the quality of the image. Studying Space Section 1 Studying Space Section 1 Telescopes, continued The diagram below shows refracting and reflecting telescopes. Studying Space Section 1 Studying Space Section 1 Sometimes you get bits of info that answer other questions in abstract articles. Students have asked where do nebulas go ? Read the article and what is or may be the answer? Studying Space Section 1 Reading check, continued What are the problems with refracting telescopes? Images produced by refracting telescopes are subject to distortion because of the way different colors of visible light are focused at different distances from the lens and because of weight limitations on the objective lens. There were other problems with earth based telescopes: Atmosphere and incidental light: Much of this has been corrected with the use of computers. Studying Space Section 1 1 – Which telescope allows for the biggest lenses 2 – Which lens would be easiest to change to increase magnification, the objective or the eyepiece? 3 – What factors affect the ability of a land based telescope to see into space? Studying Space Section 1 Telescopes, continued Telescopes for Invisible Electromagnetic Radiation • Scientists have developed telescopes that detect invisible radiation, such as a radio telescope for radio waves. • One problem with using telescopes to detect invisible electromagnetic radiation is that Earth’s atmosphere acts as a shield against many forms of electromagnetic radiation. • Ground-based telescopes work best at high elevations, where the air is thin and dry. Studying Space 1 Observing the Universe Section 1 Radio Telescopes radio telescope: A telescope that collects and amplifies radio waves. Because radio waves have long wavelengths, a radio telescope must be built with a very large objective, usually some form of dish antenna. Astronomers often build several radio telescopes close together and connect them to form one large telescope called a VLA (Very Large Array.) Studying Space Section 1 The Very Large Array, one of the world's premier astronomical radio observatories, consists of 27 radio antennas in a Y-shaped configuration on the Plains of San Agustin fifty miles west of Socorro, New Mexico. Each antenna is 25 meters (82 feet) in diameter. Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy • Spacecrafts that contain telescopes and other instruments have been launched to investigate planets, stars, and other distant objects • In space, Earth’s atmosphere cannot interfere with the detection of electromagnetic radiation. Studying Space Section 1 Reading check Why do scientists launch spacecraft beyond Earth’s atmosphere? Scientists launch spacecraft into orbit to detect radiation screened out by Earth’s atmosphere and to avoid light pollution and other atmospheric distortions. Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy, continued Space Telescopes (Do not copy- Raise your hand if you read this) • The Hubble Space Telescope collects electromagnetic radiation from objects in space as well as visible light images . • The Chandra X-ray Observatory makes remarkably clear images using X rays from objects in space, such as remnants of exploded stars. • The Swift spacecraft detects gamma rays and X rays from explosions and collisions of objects such as black holes. • The James Webb Space Telescope is scheduled to be launched in 2013 to detect near- and mid-range infrared radiation from objects in space. Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy, continued Other Spacecraft • Since the early 1960s, spacecraft have been sent out of Earth’s orbit to study other planets. • The space probes Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 investigated Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, and collected images of these planets and their moons and they are about to leave our solar system. • The Galileo spacecraft orbited Jupiter and its moons from 1995 to 2003. Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy, continued Other Spacecraft, continued • The Cassini spacecraft began orbiting Saturn in 2004. In December 2004, the Huygens probe detached from the Cassini orbiter to study the atmosphere and surface of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. • The twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity landed on Mars in January 2004. They confirmed that water had once been present on Mars. • In 2008, the Phoenix lander found ice on Mars. Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy, continued Human Space Exploration • Spacecraft that carry only instruments and computers are described as robotic and can travel beyond the solar system. • The first humans went into space in the 1960’s. Between 1969 and 1972, NASA landed 12 people on the moon. • The loss of two space shuttles and their crews, the Challenger in 1986 and the Columbia in 2003, have focused public attention on the risks of human space exploration. (Actually this is the risk of using the lowest bidder on contracts) Studying Space Section 1 Space-Based Astronomy, continued Spinoffs of the Space Program • Satellites in orbit provide information about weather all over Earth. • Other satellites broadcast television signals from around the world or allow people to navigate cars and airplanes. • Inventing ways to make objects smaller and lighter so that they can go into space has also led to improved technology. • Even medical equipment, like the heart pump, have been improved based on NASA’s research on the flow of fluids through rockets.