* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.1 law of reflection and curved mirrors
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Magic Mirror (Snow White) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
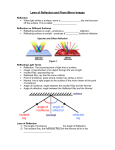
11.1 Law of Reflection and Plane Mirrors An image is a reproduction of an object produced by an optical device like a mirror When light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is aways EQUAL to the angle of reflection Incident ray – incoming ray Reflected ray – ray that bounces off a surface Normal – a dash line drawn perpendicular to a mirror at the point of reflection - its imaginary Angle of incidence (Ɵi) – angle between the incident ray and normal Angle of reflection (Ɵr) – angle between the reflected ray and normal The angle of incidence and angle of reflection are ALWAYS measured from the NORMAL Why????? Some surfaces are curved. This makes it difficult to measure a correct angle from the surface When a reflective surface generates an image, the image possesses certain characteristics: S = size An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind the mirror T= type. The image may be virtual (reflected light rays meet behind the mirror) or real (reflected light rays meet in front of the mirror and produce an image that can be projected onto a screen) A mirror with a flat reflective surface Characteristics of an image: Size= The same height as the object Attitude = Upright (same direction as object) but laterally inverted (left and right switch) Location = same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it Type = The image is VIRTUAL (reflected rays cross behind the mirror) IMAGE IS FORMED THE SAME DISTANCE BEHIND THE MIRROR AS THE OBJECT IS IN FRONT OF IT The light from an object in front of a mirror has to travel to the mirror, and then bounce off it to return to your eyes R L L R Images are reversed because light rays that hit a plane mirror are reflected right back along the same path That means a point on your left side is reflected off the right side of the mirror – therefore making it look like the image is reversed when it returns to your eyes P. 420 #1-4 Worksheet drawing reflected rays from a normal