* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Slides
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
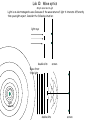
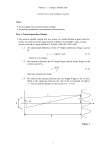
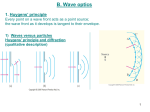
Lab 10: Wave optics Only 2 more labs to go!! Light is an electromagnetic wave. Because of the wave nature of light it interacts differently than you might expect. Consider the following situation: light rays double slits screen Wave front from light light source double slits screen D d R2 intensity maxima The maximas in intensity occur when the difference in path (from the two slits) is equal to an integral number of wavelengths. In other words, when: central maxima R n y R1 double slits screen It can be shown from trigonometry that, R d sin So then we will have points of maximums when: d sin n Where d, is the slit separation, is the angle between the maxima and the optical axis, n is the order of intensity (i.e. n = 1, 2 3, ..etc.), and is the wavelength of light. Notice that for small angles, < 5o, sin = tan , and for this situation tan is: y tan D where, y is the distance the maxima is from the central maxima, and D is the distance between the screen and the grating. d sin n So our equation becomes: Dn y d n y d D Today, you are going to measure the distance spots occur from the central maxima. From this you will be ask to calculate the slit separation and the wavelength. Let’s look at this example: White light is incident upon a regular array of slits. An interference pattern is observed on a screen, a distance of 8 meters from the slits. It is noted that the second order yellow ( = 550 nm) is at a horizontal distance of 10 cm from the center. What will be the location of the first order yellow? Dn 8m 1 550 10 9 m y d d Unfortunately, we don’t have the slit separation so we need to solve for d, first. Remember that the second order spot is found 10cm away from the center, so we can use this information to calculate d: Dn 8m2 550 109 m d 8.8 105 m y 0.1m Using this we can solve for y and we get: y = 0.05 m