* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sedimentary Rock Formation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
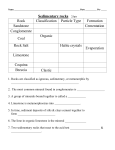
Sedimentary Rock Formation EQ: How do I identify sedimentary rocks? SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments that have been weathered, eroded and then deposited become compacted and cemented together. • Vocabulary Help 1. sediments-small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or living things. 2. weathering-wearing away or breaking down into smaller and smaller pieces 3. erosion-moving, transporting, or carrying away sediments to another place (caused mostly by wind, water, or ice) 4. deposition-place of settling 5. compaction-pressing or pushing down (caused by pressure from layers of sediments above and the weight of the water) 6. cementation-stick together and harden • Sedimentary Rock Simulation Compaction Cementation (Crystallization) Common Characteristics • most are found on the exposed surface of Earth • stratification - visible layers with oldest layer usually found on bottom • may contain fossils • Many form underwater • May have ripple marks TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 1. Detrital -forms from broken fragments of other rocks -grouped by size of particles Examples of Detrital Sedimentary Rocks • Conglomerate-large rounded sediments • Breccia-large sharp or jagged sediments Examples of Detrital Sedimentary Rocks • Sandstone-sand size particles • Siltstone-silt sized particles • Shale-tiny particles of clay or mud Found in the Real World • Sandstone TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 2. Chemical -forms from dissolved minerals that crystallize -sea or lake water evaporates leaving minerals behind that crystallize together -ex. limestone rock salt TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 3. Organic -forms from the remains of once-living things -often contains fossils Examples of Organic Sedimentary Rocks • coquina-rock completely made of shell fragments • chalk-made of microscopic shells • coal (used for energy)forms when pieces of dead plants are buried under other sediments in swamps over a period of millions of years And the rock cycle continues… • Sedimentary rock an be uplifted and exposed to the surface-possibly as parts of mountains only to be worn away again by weathering and erosion