* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
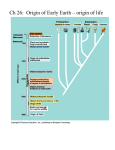
Human Anatomy and Physiology I CHAPTER 2 Chemical Basis of Life chapt2student 2-1 Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life Why study chemistry in an Anatomy and Physiology class? - ________________________________________ - cellular functions result from chemical changes - ______________________________________________ processes, and develop new drugs and methods for treating diseases chapt2student 2-2 Structure of Matter Matter – anything that takes up ___________________; composed of elements Elements – composed of chemically identical atoms • bulk elements – ____________________________ amounts • ________________ – required by the body in small amounts Atoms – ___________________________ chapt2student 2-3 Atomic Structure Atoms - composed of _________________ • protons – carry a _____________ • ________ – carry no electrical charge • electrons – carry a __________ charge Nucleus • __________________ • composed of _______ and _________ • ___________ move around the nucleus chapt2student 2-4 Atomic Number and Atomic Weight Atomic Number • number of ________ in the ________ of one atom • each element has a unique _______________ • equals the number of electrons in the atom Atomic Weight • the number of ________ plus the number of __________ in one atom • __________ do not contribute to the weight of the atom chapt2student 2-5 Isotopes Isotopes • atoms with the same _____________ but with different atomic weights • atoms with the same number of ________ and __________ but a different number of neutrons • oxygen often forms isotopes (O16, O17, O18) • unstable isotopes are ____________; they emit subatomic particles chapt2student 2-6 Molecules and Compounds ___________ – particle formed when two or more atoms chemically combine Compound – particle formed when two or more ___________________ elements chemically combine Molecular formulas – depict the elements present and the number of each atom present in the molecule H2 C6H12O6 H2O chapt2student 2-7 Electrons • found in regions of space called ________________ (energy shells) • each shell can hold a _____________________________ • for atoms with atomic numbers of ________, the following rules apply: • the first shell can hold up to _________ • the second shell can hold up to __________ • the third shell can hold up to ______________ • lower shells are filled first • _____________________________________ chapt2student 2-8 Ions Ion • an atom that has ______________________(s) • an electrically charged atom • _________________________ become stable Cation • a ________ charged ion • formed when an atom _______________ Anion • a ________________ charged ion • formed when an atom gains an chapt2student electron(s) 2-9 Ionic Bond Ionic Bond • an attraction between a ___________________ • formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom chapt2student 2-10 Covalent Bond ________________________________ •____________ atoms form ____________ •_________ atoms form ____ bonds •Nitrogen atoms form three bonds •______________ form _____ bonds chapt2student H―H O=O N≡N O=C=O 2-11 Structural Formula Structural formulas ________________________ arranged in various molecules chapt2student 2-12 Polar Molecules Polar Molecule • molecule with a _____________ end and a slightly positive end • results when electrons are ___________ equally in covalent bonds • water is an important polar molecule chapt2student 2-13 Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen Bond • a ________________ between the positive end of one __________________ and the negative end of another polar molecule • formed between _______________ • important for ________ and nucleic acid structure chapt2student 2-14 Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions occur when ________________ form or break among atoms, ions, or molecules Reactants are _______________________ by the chemical reaction Products are _____________ formed at the end of the chemical reaction NaCl Na+ + ClReactant Products chapt2student 2-15 Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis Reaction – ________________ are formed A + B AB Decomposition Reaction – chemical bonds are __________ AB A + B Exchange Reaction – chemical bonds are _________ and ______ AB + CD AD + CB Reversible Reaction – the products can __________ to the reactants A + B n AB chapt2student 2-16 Acids, Bases, and Salts Electrolytes – substances that release __________ NaCl Na+ + Cl- Acids – __________ that release hydrogen ions in water HCl H+ + Cl- Bases – substances that ____________ that can combine with ________________ NaOH Na+ + OH- Salts – ____________ formed by the reaction between an _____________ HCl + NaOH H2O + NaCl chapt2student 2-17 Acid and Base Concentrations _________ - indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution Neutral – ____; indicates equal concentrations of H+ and OH- Acidic – pH less than 7; _________________ concentration of ___ Basic or alkaline – pH ______________; indicates a greater concentration chapt2student of ___ 2-18 Organic Versus Inorganic Organic molecules • contain __________ • usually larger than __________ molecules • dissolve in ______ and ____________ • ____________, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Inorganic molecules • generally __________________ • usually _________ than organic molecules • usually ______________ or react with water to release ions • water, _______, ___________, and inorganic salts chapt2student 2-19 Inorganic Substances Water • most abundant compound in living material • _____________ of the weight of an adult human • major component of all body fluids • ___________________________________ • important role in transporting chemicals in the body • can absorb and transport heat Oxygen (O2) • used by _____________ to release energy from nutrients • necessary for survival 2-20 chapt2student Inorganic Substances Carbon dioxide (CO2) • __________________ released during metabolic reactions • must be removed from the body Inorganic salts • ___________________ • sources of necessary ions (___, ___, ___, Ca2+, etc.) • play important roles in _________________ chapt2student 2-21 Organic Substances Carbohydrates • provide _______________ to cells • supply materials to build cell structures • water-soluble • contain ____________ • ratio of H to O close to 2:1 (C6H12O6) • __________________ – glucose, fructose • disaccharides – _______, _______ • ________________ – glycogen, cellulose chapt2student 2-22 Organic Substances Carbohydrates chapt2student 2-23 Organic Substances Lipids • soluble in organic solvents • fats (_______________) • used primarily for ______ • contain C, H, and O but less O than carbohydrates (C57H110O6) • building blocks are __________ and __________ per molecule • saturated and unsaturated chapt2student 2-24 Organic Substances Lipids • phospholipids • building blocks are 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and 1 phosphate per molecule • ___________________________ • ______________________________ chapt2student 2-25 Organic Substances Lipids • steroids • connected _______________ • component of _________________ • used to ___________________ • cholesterol chapt2student 2-26 Organic Substances Proteins • structural material • ________________ • ___________ • ___________ • __________ • ___________ • building blocks are __________ chapt2student • amino acids held together with _________ bonds 2-27 Organic Substances Proteins Four Levels of Structure chapt2student 2-28 Organic Substances Nucleic Acids • constitute genes • play role in _________________ • building blocks are _____________ • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double polynucleotide • RNA (ribonucleic acid)chapt2student – single polynucleotide 2-29 Organic Substances Nucleic Acids chapt2student 2-30 Clinical Applications Radioactive Isotopes Reveal Physiology • injected into the body • different types taken up by different organs • can be detected in the body using a scintillation counter • can be used to destroy specific tissues • commonly used • _______-131 for thyroid function • thallium-201 for heart function • gallium-67 and cobalt-60 for cancer • others used to assess kidney functions, measure hormone levels and bone density changes chapt2student 2-31