* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Can the sun make it rain, or (Will astronomy help us
Main sequence wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Microplasma wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
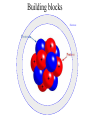
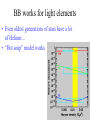
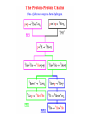
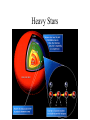
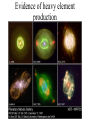
TOPS June 21, 2001 - Origins? Where did all this stuff come from? (What astronomy has to say about it?) Jeff Kuhn, IfA [email protected] Substance? • Molecules, compounds • Atoms, elements • Fundamental atomic constituents Forces for change • Thermodynamics • Chemistry • Life Building blocks Electrons Elements Nuclear building blocks and “patterns” Cosmic abundances Solar system abundances Very local abundances Most common compound: Water! CNO Fe Most common elementary particle: Pb Neutron, almost same as protons, IDENTICAL number of electrons Element origins • Where does it start (Big Bang?) • Did it all come from the first 3 minutes? – Can stars play a role? A brief history Epochs BB works for light elements • Even oldest generations of stars have a lot of Helium… • “Hot soup” model works Making He in the sun... Heavy Stars Evidence of heavy element production Heavy elements require more... • Higher densities and temperatures… • Above Iron need something special to happen… Heaviest elements from cosmic explosions (Supernovae) • SN1987A was the first Supernovae in hundreds of years that was visible by eye Molecule problems... • Collisions aren’t frequent enough to get atoms to stick…Need a way to collect atoms so they can combine… • Cosmic dust is the answer... Molecules and solids? We see dust/molecules around giant stars Dust and gas are always found together! ISO image of HD97300 Where did we come from then? Summary • Light elements formed in the first 3 minutes • Heavies formed in stars later and now • Dust (grains) formed in cool parts of giant stars • Molecules formed on dust grains • Planets condensed from stellar environment • Biological processes differentiated elements Web resources – www.pbs.org/deepspace/timeline/index.html • Big Bang, classroom activities, screen savers – howstuffworks.lycos.com/atom.htm • activities, atoms, general science, *links* – micro.magnet.fsu.edu • higher level science, movies, Electricity/Mag – www.lbl.gov/abc/wallchart/index.html • Nuclear science intro – – – – – www.iso.vilspa.esa.es/science/ btc.montana.edu/ceres/html/stars1.html#lessonplans helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/nucleo.html#nucactys www.ncsa.uiuc.edu/Cyberia/Bima/SolSys.html www.eng.rpi.edu/~napolj/Origins – this power point presentation at hubble.ifa.hawaii.edu, anonymous ftp on directory INCOMING named topsorigins.ppt Activities • Concepts – – – – Atoms as product of matter subdivision Atoms mostly space, nucleus+electrons Fission requires high density and temperature “Cross-section” concept • protons and neutrons different cross-sections – Molecules built from atoms – Local constituents result from “fractionation” Activities • Making atoms, 10cm paper strip cut 31 times… • Make cardboard atom target. Rice grain nucleus, 3’ diameter circle • Proton and neutron target practice, making He • Atomic differentiation, rice and bb’s for H and Fe