* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNEP-UNECE cooperation in a changing world on water, climate
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
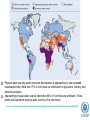
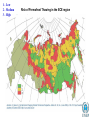
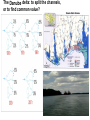
UNEP-UNECE cooperation in a changing world on water, climate change and security related issues Panel 2: UNECE Acting on Climate: Water, Forestry and Timber UNECE 63rd Session, Palais des Nations, Geneva 31 March 2009 J.C. Bouvier Director and Regional Representative UNEP Regional Office for Europe Presentation overview • Illustration of some global challenges • The perspective of UN Reform and international environmental governance for the ECE region • Concrete examples of joint UNEP-UNECE work in the ECE region: Environment for Europe process, Transport & Energy, Forestry and Timber, Environmental Performance Reviews, Environment and Security (ENVSEC) activities Water Stress Physical water scarcity (water resources development is approaching or has exceeded sustainable limits). More than 75% of river flows are withdrawn for agriculture, industry, and domestic purposes. Approaching physical water scarcity. More than 60% of river flows are withdrawn. These basins will experience physical water scarcity in the near future. Source: Comprehensive assessment of water management in Agriculture, International Water Management Institute 2007 1 – Low 2 – Medium 3 – High Risk of Permafrost Thawing in the ECE region Permafrost thawing: Economic damage and risk to infrastructure Enhanced cooperation between UN organisations • Ongoing international environmental governance debates in New York (UNGA 2008) and Nairobi (last UNEP GC Ministerial debate on IEG: help or hindrance? February 2009) and the CSD WG (Mexico, Switzerland) recommended action at regional level • Meanwhile Geneva demonstrated a range of experiences of UNEP and UNECE working together on several environmental issues i.e. facilitating implementation of UNECE conventions, assessments (EPR) & monitoring • Joint efforts towards ‘Green Economy’ between UNECE and UNEP • An annual joint review – enhanced as of 2009 to broaden its scope • UNECE leadership in RCM and interaction with RDT key to success. UNEP committed. Some concrete examples of UNECE-UNEP collaboration • Environment for Europe Ministerial process started in Dobris 1991, latest Belgrade 2007. Support to UNECE as Secretariat and specific UNEP tasks (i.e. SCP, PEBLDS) • Environmental performance reviews: Uzbekistan (2009), previously in Azerbaijan, Yugoslavia, Tajikistan • Also with WHO: Transport, Health and Environment Pan-European Programme (THE PEP) • Energy Efficiency 21 Project with UNEPGEF: to promote the formation of a market for energy efficiency and foster financing for energy efficiency investments in the EECCA • Caspian Environment Programme: Transboundary EIA protocol (with ESPOO Convention) • ENVSEC activities within ECE region: Dniester, Danube delta & the Upper Pripyat The Danube delta: to split the channels, or to find common value? The Dniester: Pollution, floods, hydro-power, politics and cooperation Climate Change in Eastern Europe Environment & Security Initiative 2009 • One direct consequence of climate change is increasing floods. Floods in summer of 2008 devastated parts of Ukraine and Moldova (material damage, destroyed infrastructure, flooded houses, dislocated populations). • There are indications that this will continue, especially with the background of illegal logging in Carpathian forests that otherwise could be natural adaptation mechanisms. Climate change in Central Asia Environment & Security Initiative 2009 • With climate change and melting glaciers in the mountains, water flow will be less stable and in the end less abundant. • Up-to-date information about what will happen to the region's water resources is needed. • Better institutions to manage water allocation, energy and agricultural use of water; understanding of humanitarian consequences (natural disasters, ‘agri-failures’, migration, local tensions and possible unrest). Thank you! www.unep.org