* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are the symptoms of SARS?
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
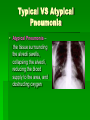
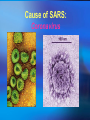
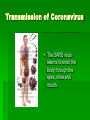
SARS Ti-Sheng (Dean) Shiune Ivy Leong SARS • What we know about SARS • What are the symptoms of SARS • How does SARS spread • Cause of SARS • Treatments on SARS What We Know About SARS Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Viral infection Affected all age group Suspected to have originated in Guandong, China Cause atypical pneumonia in infected patients Typical VS Atypical Pneumonia Typical Pneumonia – a lung infection, where the alveoli in the affected area fill up with exudates Typical VS Atypical Pneumonia Atypical Pneumonia – the tissue surrounding the alveoli swells, collapsing the alveoli, reducing the blood supply to the area, and obstructing oxygen What are the symptoms of SARS? High fever ( > 380C) Headache, general feeling of discomfort Cough, nasal congestion, sneezing Severe muscle and joint pain Difficulty in breathing Continuous localized pain in the chest, which increases when taking a breath How does SARS spread? Close person-to-person contact Physical contact with something that has been contaminated by a SARS patient (such as droplets) Incubation period After the virus enters the body, it requires 3 to 10 days incubation period before the disease appears Cause of SARS: Coronavirus Coronavirus Family Halo or crown-like (corona) virus Cause mild to moderate respiratory illnesses such as common cold Able to survive in dry air for up to 3 hours Can be killed by exposure to ultra-violet light Mutate easily, and each mutation triggers off an epidemic of respiratory disease Transmission of Coronavirus Airborne Transmission : Coronavirus family has the property of surviving in dry air/surfaces for up to 3 hours. In these conditions, the virus crystallizes, and can float in the air like dust. Transmission of Coronavirus The SARS virus seems to enter the body through the eyes, nose and mouth. Treatments on SARS Recent Treatments: • Antivirals such as oseltamivir or ribavirin • Steroids (orally or intravenously) in combination with ribavirn and other antimicrobials Being developed