* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hand, Wrist & Fingers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
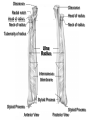
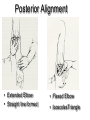
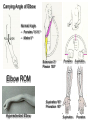
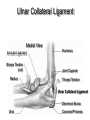
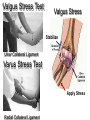
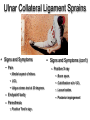
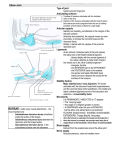
Elbow Injuries • Critical link in kinetic chain of upper extremity • Extremely susceptible to injury – Big range of motion – Weak lateral bone structure – Boney anatomy prominent causing soft tissue damage – Excessive stress on joint from sports – Locking motion of some activities – Use of implements – Throwing motion Olecranon Olecranon Radial notch Head of radius Neck of radius Head of radius Neck of radius Tuberosity of radius Ulna Radius Interosseous Membrane Styloid Process Styloid Process Anterior View Styloid Process Styloid Process Posterior View Posterior Alignment • Extended Elbow • Straight line formed • Flexed Elbow • IsoscolesTriangle Carrying Angle of Elbow Normal Angle – Females 10-15 º – Males 5 º Extension 0º Flexion 150º Pronation Supination Elbow ROM Supination 90º Pronation 90º Hyperextended Elbow Supination Pronation Ulnar Collateral Ligament Medial View Annular Ligament Biceps Tendon (cut) Radius Humerus Joint Capsule Triceps Tendon Ulnar Collateral Ligament Olecrenon Bursa Ulna Coronoid Process Valgus Stress Test Valgus Stress Stabilize Ulnar Collateral Ligament Varus Stress Test Apply Stress Radial Collateral Ligament Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprains • Etiology – Valgus force – Repetitive trauma – Related injuries • Ulnar nerve inflammation • Wrist flexor tendinitis • Overuse flexor/pronator strain • Elbow flexion contractures • Instability Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprains • Signs and Symptoms – Pain • Medial aspect of elbow • UCL • Valgus stress test at 20 degrees – End-point laxity – Paresthesia • Positive Tinel’s sign • Signs and Symptoms (con’t) – Positive X-ray • Bone spurs • Calcification w/in UCL • Loose bodies • Posterior impingement • Management – Conservative treatment • RICE • NSAID’s – W/ resolution • Strengthening • Analysis of the throwing motion – Surgical intervention • Reconstruction • (Tommy John procedure) • Return to activity 22-26 weeks post op Lateral Epicondylitis Tennis Elbow – Etiology • Repetitive microtrauma • Insertion of extensor/supinator muscle/s • Lateral epicondyle – Signs and Symptoms • Aching pain after activity • Pain w/ resistive wrist extension • Weakness in wrist and hand • Elbow decreased ROM Assessment Management • RICE • NSAID’s • Analgesics • Rehabilitation – ROM exercises – PRE Resisted Eccentric Contraction – Deep friction massage – Stretching in pain free ROM • Mechanics training • Bracing – Counter force brace – Neoprene sleeve • Superficial location • Extremely susceptible to injury Olecrenon Bursitis • Etiology – Direct blow – Irritation to bursa • Chronic irritation – Production of fluid – Increased capillary permeability – Fluids and exudates flow into the bursa – Bursal wall thickens over time – May have irregular areas of scar tissue • Feels like loose joint cartilage (joint mice) • Calcium deposits – Acutely injured joint • Blood may fill the bursa • Risk of infection