* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
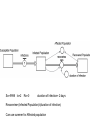
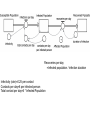
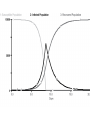
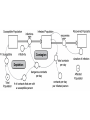
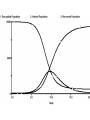
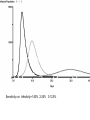
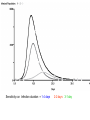
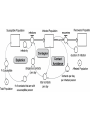
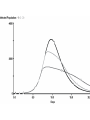
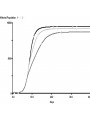
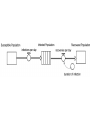
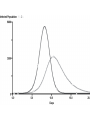
Chapter 8 SIR Models So=9998 Io=2 Ro=0 duration of Infection= 2 days Recoveries=(Infected Population)/(duration of infection) Can use summer for Affected population Recoveries per day =Infected population / infection duration Infectivity (rate)=0.25 per contact Contacts per day=6 per infected person Total contact per day=6 * Infected Population Sensitivity Analysis • Contact number = (infectivity) (contacts per day) (infection duration) Sometimes referred to at Ro the reproductivity number (The number of new infections) / (a single infected person) R>1 epedemic R<1 disease dies out Sensitivity run Infectivity=1-50% 2-25% 3-12.5% Sensitivity run Infection duration = 1-4 days 2-2 days 3-1 day Policy analysis • What can we do?? 1918 influenza pandemic 50 to 100 million died worldwide 1918 Influenza: the Mother of All Pandemics Jeffery K. Taubenberger* and David M. Morens Emerging Infectious Diseases • www.cdc.gov/eid Vol. 12, No. 1, January 2006