* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lookback study in Japan
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
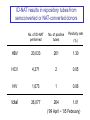
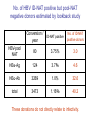
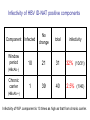
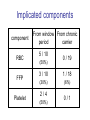
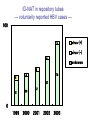
Lookback study for transfusionrelated HBV infection in Japan Tokyo Metropolitan Red Cross Blood Center Masahiro Satake Lookback study in Japan • Aliquots from all donations have been stored since 1997. • When necessary, each aliquot was investigated using individual donation-NAT (ID-NAT). • Subjects for the study : converters for HBs-Ag, HBc-Ab, HCV-Ab, HIV-Ab, screening NAT for HBV, HCV or HIV during April 1999 and February 2005 ID-NAT results in repository tubes from seroconverted or NAT-converted donors No. of ID-NAT performed No. of positive tubes Positivity rate (%) HBV 20,033 261 1.30 HCV 4,371 2 0.05 HIV 1,673 1 0.06 total 26,077 264 1.01 (‘99 April ~ ’05 February) No. of HBV ID-NAT positive but pool-NAT negative donors estimated by lookback study Conversion / year ID-NAT positive No. of ID-NAT positive donors HBV-pool NAT 80 3.75% 3.0 HBs-Ag 124 3.7% 4.6 HBc-Ab 3269 1.0% 32.6 total 3473 1.16% 40.2 These donations do not directly relate to infectivity. The infectivity of HBV-ID-NAT positive components No. of ID-NAT positive donation No. of components released transfused・・・・・・・・・・・ discarded・・・・・・・・・・・ unknown・・・・・・・・・・・ 267 321 293 16 12 Outcome of transfused patients(191 reports available ) HBs-Ag conversion 6 HBV-DNA conversion 2 HBs-Ab conversion 3 positive, but no information before transfusion 7 markers not changed 60 dead 99 discharged etc. 14 The infectivity of HBV-ID NAT-positive components HBV infected 11 Undetermined 7 No change 60 others 115 Infectious risk when transfused with ID-NAT positive blood 11/78~18 /78 6~10 HBV infections per year Infectivity of HBV ID-NAT positive components Component Infected No change Window period 10 21 31 32% (10/31) 1 39 40 2.5% (1/40) total infectivity (HBcAb -) Chronic carrier (HBcAb +) Infectivity of W.P. component is 13 times as high as that from chronic carrier. Implicated components component RBC FFP Platelet From window From chronic period carrier 5 / 10 (50%) 0 / 19 3 / 10 1 / 18 (30%) (6%) 2/4 (50%) 0/1 Established cases for HBV infection Disorders of patients hematologic malignancy gastric cancer dissecting aortic aneurysm shock due to multiple trauma rheumatoid arthritis unknown 2 2 1 1 1 4 ID-NAT in repository tubes --- voluntarily reported HBV cases --100 4 virus (+) virus (-) 4 unknown 5 6 75 4 57 31 36 1999 2000 42 0 2001 2002 2003 The risk of HBV infection under current screening algorism including 50p-NAT system Sources HBV-infection Lookback investigation 6~10 Voluntary report of infection 5 total 11~15 cases/year Lookback study for HCV and HIV No. of ID-NAT performed HCV 4,371 HIV 1,673 No. of positive tubes 2 (1 donation before NAT implementation) 1 (Established infected case) Seroconversion possibly due to nonspecific reaction was also subjected to lookback study. Estimates for the Occurrence of TransfusionTransmitted Viral Diseases in Japan • HBV HBV+ donation detectable only by ID-NAT : 1 / 150,000 11~15 infection cases per year (1 infection / 3.6~5.4 x 105 components) • HCV (difficult to estimate) HCV+ donation detectable only by ID-NAT : 1 / 24 million (1 component / 4 years) • HIV (difficult to estimate) HIV+ donation detectable only by ID-NAT : 1 / 12 million (1 component / 2 years)