* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
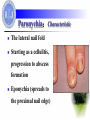
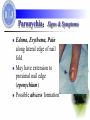
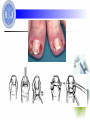
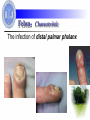
Hand Infection Dr. Weiguo Hu 胡伟国 Dr. Weihua Qiu 邱伟华 Department of Surgery Rui Jin Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Background: Anatomy factors Multiple compartments and planes in hand Infections are dictated by fascial boundaries in hand Classifications:Characteristic Paronychia Felon Tenosynovitis Deep fascial space infections Paronychia:Characteristic The lateral nail fold Starting as a cellulitis, progression to abscess formation Eponychia (spreads to the proximal nail edge) Paronychia:history Recent trauma to lateral nail fold Nail biting Manicuring Dishwashing Finger sucking (children) Paronychia:Signs & Symptoms Edema, Erythema, Pain along lateral edge of nail fold May have extension to proximal nail edge (eponychium) Possible abscess formation Etiology: Microorganism Staphylococcus & Streptococcus in most cases Mycobacteria and fungi in chronic cases or immunocompromised patients Anaerobes in the pediatric population due to finger sucking. Management: If no frank abscess frequent hot soaks & antibiotics If pus is present incision and drainage If pus has tracked beneath the nail remove an adjacent longitudinal section If eponychia is resulted remove the entire nail plate Complications: Eponychia (Subungual abscess ) Osteomyelitis of the distal phalanx Development of a felon Chronic infection Prognosis: Most resolve in 2-4 days Chronic infections are likely fungal infections. Felon:Characteristic The infection of distal palmar phalanx Felon:Characteristic Compartmentalized infection Increased pressure within the closed compartment Impaired venous outflow a local compartment syndrome and myonecrosis and osteomyelitis Etiology: Microorganism Staphylococcus & Streptococcus is the most common causative organism Typically direct inoculation of bacteria by penetrating trauma May be caused by hematogenous spread Local spread from an untreated paronychia Felon:Signs & Symptoms Recent trauma to finger pad or paronychia Typically Throbbing Pain Swelling, Pressure, Erythema Felon:Signs & Symptoms Painful, Tense, Erythematous finger pad Pointing of abscess possibly present Signs typically limited to area distal to the distal interphalangeal joint Evidence of penetrating trauma Incision & Drainage Frank abscess & tense finger pad is the indication A longitudinal incision over the area of greatest fluctuance To avoid penetration of the tendon sheath, the incision should not extend to the distal interphalangeal crease Using a hemostat, bluntly dissect the wound to promote drainage Irrigating the cavity copiously and loosely pack with a gauze wick. Incision & Drainage scarring sensory loss unnecessary pain instability of the finger pad spread of infection into the adjacent tendon sheath. Felon:Follow up Reevaluate the wound 48 hours after initial incision If continued drainage is present, loosely repack the wound If no further drainage is present, repacking is unnecessary Continue antibiotics for 5-7 days The prognosis is good, with healing in 1-2 weeks Complications: Osteomyelitis Necrosis Sinus tract formation Septic joint Tenosynovitis Infectious Tenosynovitis The tenosynovial coverings of the second, third, and fourth digits do not communicate with either the radial or ulnar bursae in most individuals Infection within a tendon sheath usually is the result of direct inoculation of bacteria from penetrating trauma. Infectious Tenosynovitis Recent penetrating trauma to hand Gonococcal infection, particularly disseminated infection Pain, especially with passive extension of finger Edema of entire finger Variable history of fever Infectious Tenosynovitis Tenderness along the course of the flexor tendon Symmetric edema of involved finger Pain on passive extension (the most important sign) Flexed resting posture of finger All 4 signs possibly not present early in the course of infection May have associated lymphangitis, lymphadenopathy, and fever Complications: Tendon destruction Functional disability Extension of infection to deep fascial space Deep fascial space infections midpalmar space thenar space dorsal subaponeurotic space subfascial web space Deep fascial space infections Recent penetrating trauma to hand or untreated tenosynovitis Palmar blister (may result in subfascial web space abscess) Pain and edema of hand Pain with movement of fingers Variable history of fever Midpalmar space infections Pain, swelling, loss of palmar concavity Pain with movement of the third and fourth digits Dorsal swelling secondary to the tracking of infection dorsally along the lymphatics Thenar space infections Marked swelling of the thumb-index web space Flexed and abducted resting posture of the thumb Pain with passive adduction Complications: Functional disability Tendon destruction Sepsis Hand loss Management: pain relief antibiotic therapy elevating and immobilizing the hand consulting an experienced hand surgeon incision and drainage Prognosis: Depending on the extention of tissue destruction bony involvement preexisting vascular insufficiency systemic complications (bacteremia, sepsis) Tons of Thanks!