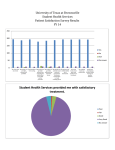
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nursing Assistant
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Nursing Assistant Principles of Asepsis Common infectious agents Microorganisms – tiny organisms that can be disease causing that can only be seen with assistance of a microscope – Bacteria – • Streptococcus – strep throat, pneumonia • E coli – urinary tract infections • Tuberculosis – lung disease – Virus – • • • • • HIV – acquired immune deficiency syndrome Hepatitis A, B, C – liver disease ( Hep B – 3 shots) Common cold – respiratory infection Influenza – fever, chills, body aches Herpes zoster - shingles Microorganisms Fungi – – Tinea pedis – athlete's foot – Candida albicans – yeast infection Insects – Lice – body, head, pubic, causes itching – Scabies – skin rash Antibiotic resistant bacterial infections – Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) – Vancomycin resistant enterococcus (VRE) Conditions necessary for infectious agent growth Food source Moisture Oxygen or lack of oxygen Warmth Darkness Six parts of chain of infection Causative agent – bacteria, fungi, virus, insects Reservoir – resident, health care worker, environment, equipment Portal of exit – excretions, wound drainage, urine, feces, blood, saliva Method of transmission – airborne, droplet, contact, food/water, animals or insects Portal of entry – non-intact skin, mucus membranes, respiratory tract, urinary tract, reproductive tract Susceptible host – resident, health care worker, families, visitors Chain of infection All parts of the chain are linked To stop the spread of infection, BREAK THE CHAIN AT ANY LINK!!!! 4 lines of defense against infection Normal flora Skin Mucus membranes Immune system – immunity & vaccines – Hepatitis B immunizations very important for HCP Signs & Symptoms of infection Appetite loss Pain Diarrhea Drainage Fatigue FEVER Nausea, vomiting Rash Redness Swelling, tenderness Asepsis vs sterile technique Medical asepsis/clean techniques – Free from microorganisms carrying disease – Handwashing – Disinfection – process of destroying pathogens utilizing soap/water or disinfectants Surgical asepsis/sterile technique – Use of sterilized equipment – all microorganisms have been destroyed – Use barriers to prevent transmission of infectious agents Role of CDC & OSHA CDC – Center for Disease Control & Prevention – Located in Atlanta, GA – Under DHHS (fed) – Makes non-regulatory recommendations for disease control – Introduced standard precautions & transmissionbased precautions in 1996 OSHA – Occupational Safety & Health Administration – Publishes & endorses rules to keep workers safe, including infection control (state – Requires written documentation & follow-up on exposure accidents Standard Precautions Noscomial infections – hospital acquired infection Standard Precautions – used for the care of all residents regardless of diagnosis or presumed disease status Designed to reduce risk of transmission of microorganisms from moist body fluids – Blood – All body fluids, secretions, excretions except sweat – Non-intact skin – Mucus membranes Standard Precautions Contamination – process by which an object, person, or area becomes unclean Methods of prevention – Handwashing • • • • • • • Beginning & end of shift Between residents After using bathroom Before handling food After removing gloves After covering mouth, nose when coughing or sneezing When providing toothbrushes, drinking glasses, towels, washclothes • Prior to handling raw fruit & vegies before serving • May substitute alcohol foams/gels during procedures involving mutiple resident contacts. Not recommended if soiled by blood/body fluids Standard Precautions Sharps disposal – Needles are never bent, broken, or recapped by hand – Dispose in appropriate Sharps containers Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) – Gloves are required: • Contact with blood, body fluids, dressings, tissues, or contaminated surfaces • Contact with non-intact skin or mucus membranes • Remove gloves when contact complete & wash hands • If gloves are torn/punctured, remove them • Change gloves between residents • Don’t reuse gloves Personal Protective Equipment Double gloves – required when necessary & according to policy Gowns or aprons – Need moisture resistant gowns when possibility of soiling with blood or body fluids – Remove when procedure complete & prior to leaving room Facial protection – Wear – masks, goggles, face shields to protect eyes, nose, mouth Environmental Controls Use EPA registered disinfectant on solid surfaces including floors, furniture, bathrooms, utility rooms Reusable equipment must be cleaned or disinfected before reuse Mouthpieces for resuscitation necessary Wastes & soiled linen should be placed in plastic bags & disposed of according to policy Wipe up body fluid spills immediately, disinfect Don’t eat, drink, apply make-up, or handle contacts Label- biohazard for sharps & blood Watch for lab specimens, label & transport Transmission-based precautions Used for residents known or suspected to be infected with pathogens transmitted by – – – – Airborne Droplet Contact Contaminated surfaces Isolation needed to separate resident to prevent spread of microorganisms Used in addition to standard precautions Type of precaution dependent on type of organisms CDC guidelines to be used Psychological effect of transmission-based precautions Interference with basic needs – safety, love, self-esteem, self actualization Methods of assisting resident to meet needs – Explain reason for isolation – Frequently check on resident & condition – Provide resident with distractions – books, tv, magazines – Instruct family & visitors on isolation techniques – Make sure equipment necessary is available – Call light in reach & answered promptly – Talk with resident when in room giving care Skills Distributing ice & water Hand washing Gloving, Gowning, & masking – – – – – – – – – Wash hands Gown – top tie first, then bottom Mask – top tie first, then bottom Gloves Do care Remove Gloves, wash hands Remove Mask – bottom tie first, then top Remove gown – bottom tie first, then top Wash hands