* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
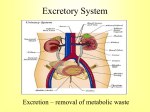
Urology & Nephrology Sections Anatomy and Physiology General Mechanisms of Nontraumatic Tissue Problems General Pathophysiology, Assessment, and Management Renal and Urologic Emergencies Anatomy & Physiology The Urinary System Female Male Urology & Nephrology The Kidneys Anatomy & Physiology The Kidneys Hilum Medulla Pyramids Papilla Renal Pelvis Anatomy & Physiology Nephrons Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Proximal Tubule Loop of Henle Distal Tubule Collecting Duct Anatomy & Physiology Functions of the Kidneys Forming and Eliminating Urine Maintaining blood volume with proper balance of water, electrolytes, and pH. Retaining key compounds such as glucose, while excreting wastes such as urea. Controlling Arterial Blood Pressure Regulating Erythrocyte Development Anatomy & Physiology Formation of Urine Glomerular Filtration GFR Reabsorption & Secretion Simple diffusion and osmosis Facilitated diffusion • Active transport Anatomy & Physiology Tubular Handling of Water and Electrolytes Diuresis and Antidiuresis Tubular Handling of Glucose and Urea BUN and Creatinine Control of Arterial Blood Pressure The Renin-Angiotensin System Control of Erythrocyte Production Erythropoietin Anatomy & Physiology Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra Testes Epididymus and Vas Deferens Prostate Gland Penis General Mechanisms of Nontraumatic Tissue Problems Inflammatory or Immune-Mediated Disease Infectious Disease Physical Obstruction Hemorrhage General Pathophysiology, Assessment and Management Differentiating GI and Urologic Complaints Pathophysiologic Basis of Pain Causes of Pain Types of Pain Visceral pain Referred pain Assessment and Management Scene Size-up Initial Assessment Focused History OPQRST History Prior History of Similar Event History of Nausea, Vomiting, and Weight Loss Change in Bowel Habits and Stool Last Oral Intake Presence of Chest Pain Assessment and Management Physical Exam Appearance Uncomfortable appearance. Posture Lying with knees drawn up. Relief with walking. Level of Consciousness Determine if changes are acute or chronic. Assessment and Management Apparent State of Health Skin Color Examination of the Abdomen Inspection for distention, ecchymosis, or scarring Pain associated with percussion of abdomen Palpation • Normal or ectopic pregnancy • Masses Assessment Tools Vital Signs Assessment and Management Management Airway, Breathing Circulation Pharmacologic Interventions IV access and analgesics. Nonpharmacological Interventions Nothing by mouth (NPO). Maintain position of comfort. Reassess mental status and vital signs frequently. Transport Considerations Renal and Urologic Emergencies Risk Factors Older Patients History of Diabetes History of Hypertension Multiple Risk Factors Renal and Urologic Emergencies Acute Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failure Renal Calculi Urinary Tract Infection Acute Renal Failure Pathophysiology Prerenal Acute Renal Failure Dysfunction before the level of kidneys • Most common and most easily reversible Renal Acute Renal Failure Dysfunction within the kidneys themselves Postrenal Acute Renal Failure Dysfunction distal to the kidneys Acute Renal Failure Acute Renal Failure Assessment Focused History Change in urine output Swelling in face, hands, feet, or torso Presence of heart palpitations or irregularity Changes in mental function Acute Renal Failure Physical Assessment Altered mental status Hypertension Tachycardia ECG indicative of hyperkalemia Pale, cool, moist skin Acute Renal Failure Physical Assessment Edema of face, hands, or feet Abdominal findings dependent on the cause of ARF Acute Renal Failure Management Airway, Breathing, Circulation IV Access Protect fluid volume. Positioning and Transport Chronic Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failure Permanent Loss of Nephrons End-Stage Renal Failure (ESRF) Pathophysiology Similar to Renal ARF Microangiopathy, glomerular injury Tubular cell injury Insterstitial injury Chronic Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failure Impairment of Kidney Functions Maintenance of blood volume with proper balance of water, electrolytes, and pH • Increased sodium, water, and potassium retention Retention of key compounds such as glucose with excretion of wastes such as urea • Loss of glucose and buildup of urea within the blood Control of arterial blood pressure • Disruption of the renin-angiotensin loop resulting in HTN Regulation of erythrocyte development • Development of chronic anemia Chronic Renal Failure Assessment Differentiate chronic and acute problems. Focused history and physical exam. Gastrointestinal complaints Changes in mental status Marked abnormalities during physical exam Uremic frost Chronic Renal Failure Chronic Renal Failure Immediate Management Monitor and support ABCs. Establish IV access. Regulate fluid volume. Monitor vital signs and cardiac rhythm. Expedite transport to an appropriate facility. Chronic Renal Failure Long-Term Management Renal Dialysis Hemodialysis Common complications Chronic Renal Failure Long-Term Management Renal Dialysis Peritoneal dialysis Common complications Renal Calculi Pathophysiology Results when “too much insoluble stuff” accumulates in the kidneys. Stone types Calcium salts Struvite stones Uric acid Cystine Renal Calculi Assessment Focused History Severe pain in one flank that increases in intensity and migrates from the flank to the groin Painful, frequent urination with visible hematuria Prior history of calculi Physical Exam Difficult due to patient discomfort Tachycardia with pale, cool, and moist skin Renal Calculi Management Maintain ABCs. Maintain position of comfort. Establish IV access. Fluid bolus may promote stone movement and urine formation. Consider medication administration. Parenteral narcotic analgesics may be indicated. Urinary Tract Infection Pathophysiology Risk Factors Increased risk in female or catheterized patients Sexual activity Lower and Upper UTIs Urethritis Cystitis Prostatitis Pyelonephritis Community-acquired vs. nosocomial infections Urinary Tract Infection Assessment Focused History Abdominal pain Frequent, painful urination A “burning sensation” associated with urination Difficulty beginning and continuing to void Strong or foul-smelling urine Similar past episodes Urinary Tract Infection Physical Exam Restless, uncomfortable appearance. Presence of a fever. Vital signs vary with degree of pain. Management Maintain ABCs. Establish IV access. Consider analgesics. Transport to appropriate facility. Urology and Nephrology Anatomy and Physiology General Mechanisms of Nontraumatic Tissue Problems General Pathophysiology, Assessment, and Management Renal and Urologic Emergencies