* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Path of Blood Through Body
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
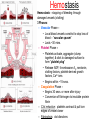
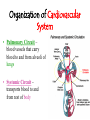
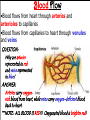
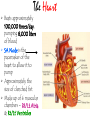
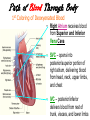
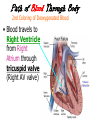
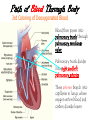
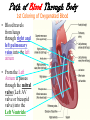
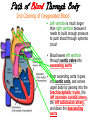
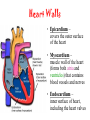
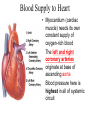
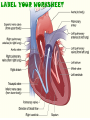
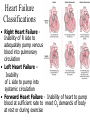
The Cardiovascular System The Lymphatic System And Respiratory System The transfer of nutrients throughout our body Some Latin Prefixes & Suffixes You Should Know! • • • • • Hemo/a-: blood Anti-: against Erythros-: red Leukos-: white -cyte: cell • -penia: poverty, not enough • -osis: too many • Thrombos-: clot • -stasis: halt, stop Blood… the fluid of the cardiovascular system • Provides to cells/tissues: – – – – – Nutrients Oxygen (O2) Hormones/enzymes Removal of wastes Special cells to protect against disease & infection (WBCs & antibodies) • Regulates: http://brucemhood.files.wordpress.com/2008/09/blood_cells.jpg – pH & ion composition of cellular fluids – Clotting capabilities to restrict blood loss – Body temperature • What kind of tissue is blood? – Connective Tissue • What are the 3 “formed elements” of blood? Plasma proteins Water 92% Albumins Plasma proteins 7% Other solutes 1% • What makes blood fluid? – Plasma Plasma BLOOD Globulins Fibrinogen Formed elements Regulatory proteins Platelets Other solutes Electrolytes – Platelets – White blood cells – leukocytes (WBCs) – Red blood cells erythrocytes (RBCs) WBCs Organic nutrients Organic wastes Neutrophils RBCs 99.9% Lymphocytes Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils Functions of Blood components • RBCs – – Most abundant – Transport of O2 • WBCs – – Body’s defense mechanism against disease & infection • Platelets – – Contain enzymes important for clotting • Formed elements made through hematopoiesis • Blood… – Temperature = ~38°C (100.4°F) – 5x more viscous than water – Slightly alkaline; pH 7.357.45 – Adult male = 5-6 L – Adult female = 4-5 L Structure & Function of RBCs • Each RBC has ~280 million Hb molecules • Hemoglobin (Hb) molecule responsible for transporting O2 & CO2 to & away from tissues – Single pigment molecule of heme • Iron (Fe) ion that interacts with O2 molecule = oxyhemoglobin – Bright red • Fe not bound to O2 = deoxyhemoglobin – Dark red/burgundy Human Tetris • Antigens – – Your Blood type surface antigens (A, B & Rh) – Rh antigen (Rh factor) – Rhesus Protein • Plasma contains antibodies that will attack antigens on “foreign” RBCs – Causes agglutination (clumping together of RBCs) & hemolysis (breaking apart of RBCs) = cross-reaction Type AB (~4%) = • Blood type determined by presence universal recipients or absence of surface antigens Both Antigens A & B – Type A (~40%) • Antigen A present • Anti-B antibodies – Type B (~10%) • Antigen B present • Anti-A antibodies present Type O (~46%) = universal donors Neither Antigens A & B present Both Anti-A & Anti-B antibodies Blood Types Make sure you understand the genotypes and the Rhesus Factor for all the bloodtypes. Lecture on Bloodtypes • • • • Anemia – Shortage of RBCs or hemoglobin – Affects delivery of O2 to tissues – Can result in heart palpitations & failure Sickle cell anemia – Hemoglobin disorder caused by abnormally shaped RBCs Thalassemia – Inherited disorder resulting in mutation of hemoglobin gene – Bone marrow transplants & blood transfusions are methods used to combat the disorder Jaundice – Yellowish-brownish staining of skin & sclerae (whites of eyes) caused by high levels of chemical called bilirubin in blood – Bilirubin is a waste product that comes from old, destroyed RBCs & is removed from blood by liver (eliminated in the feces, giving it its brown color) Conditions associated with Blood Normal RBCs Sickle cell RBCs White Blood Cells (leukocytes) • Structure – – No hemoglobin • Functions – – Defend body against pathogens – Remove toxins, waste & damaged cells • Location & Movement – – Most WBCs in body in CTP or lympathic organs – Circulating WBCs only small fraction of total population – Use bloodstream as mode of transportation to area of infection/injury http://www.lymphomation.org/images/leukocytes-normal.gif Conditions associated with WBCs Leukopenia – Inadequate number of WBCs Leukocytosis – Excessive number of WBCs Leukemia – Cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal production of WBCs Platelets (aka – thrombocytes) • Functions: – Cell fragments that play major role in clotting system • Release chemicals important to clotting process • Formation of temporary patch in walls of damaged blood vessels • Active contraction after clot has formed – Continuously removed & replaced every 9-12 days by phagocytes in spleen Hemostasis • • Hemostasis – stopping of bleeding through damaged vessels (clotting) 3 Phases: – Vascular Phase – • Local blood vessels constrict to stop loss of blood – “vascular spasm” • Lasts ~30 mins. – Platelet Phase – • Platelets activate, aggragate (clump together) & stick to damaged surface to form “platelet plug” • Release ADP, thromboxane A2, serotonin, clotting factors, platelet-derived growth factors, Ca2+ ions • Begins within ~15 secs. – Coagulation Phase – • Begins 30 secs. or more after injury • Conversion of fibrinogen to insoluble protein fibrin – Clot retraction: platelets contract & pull torn edges of vessel closer – Fibrinolysis: clot dissolves Blood Detectives video & questionnaire What can blood tell us about ourselves? How is blood used in diagnosing diseases or disorders? What kinds of conditions are associated with the blood? • As you watch the Blood Detectives video, fill in your questionnaire about each patient & their condition. Organization of Cardiovascular System • Pulmonary Circuit – blood vessels that carry blood to and from alveoli of lungs • Systemic Circuit – transports blood to and from rest of body Blood Flow •Blood flows from heart through arteries and arterioles to capillaries •Blood flows from capillaries to heart through venules and veins QUESTION: Why are arteries represented in red and veins represented In blue? ANSWER: Arteries carry oxygenrich blood from heart, while veins carry oxygen-deficient blood back to heart. ***NOTE: ALL BLOOD IS RED!!! Oxygenated blood is brighter red! The Heart • Beats approximately 100,000 times/day, pumping 8,000 liters of blood • SA Node is the pacemaker of the heart to allow it to pump • Approximately the size of clenched fist • Made up of 4 muscular chambers – Rt/Lt Atria & Rt/Lt Ventricles Path of Blood Through Body 1st Coloring of Deoxyenated Blood • Right Atrium receives blood from Superior and Inferior Vena Cava • SVC – opens into posterior/superior portion of right atrium, delivering blood from head, neck, upper limbs, and chest • IVC – posterior/inferior delivers blood from rest of trunk, viscera, and lower limbs Path of Blood Through Body 2nd Coloring of Deoxygenated Blood • Blood travels to Right Ventricle from Right Atrium through tricuspid valve (Right AV valve) Path of Blood Through Body 3rd Coloring of Deoxygenated Blood • Blood then passes into pulmonary trunk through pulmonary semilunar valve • Pulmonary trunk divides into right and left pulmonary arteries • These arteries branch into capillaries in lungs, where oxygen enters blood and carbon dioxide leaves Path of Blood Through Body 1st Coloring of Oxygenated Blood • Blood travels from lungs through right and left pulmonary veins into the left atrium • From the Left Atrium it passes through the mitral valve (Left AV valve or bicuspid valve) into the Left Ventricle Path of Blood Through Body 2nd Coloring of Oxygenated Blood • Left ventricle is much larger than right ventricle because it needs to build enough pressure to push blood through systemic circuit • Blood leaves left ventricle through aortic valve into ascending aorta • From ascending aorta it goes into aortic arch, and serves upper body by passing into the brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, the left subclavian artery, and down the descending aorta Heart Walls • Epicardium – covers the outer surface of the heart • Myocardium – muscle wall of the heart (forms both atria and ventricles) that contains blood vessels and nerves • Endocardium – inner surface of heart, including the heart valves Internal/External Anatomy of Heart •Interatrial septum – wall between atria •Interventricular septum – thicker wall between ventricles APEX Blood Supply to Heart • Myocardium (cardiac muscle) needs its own constant supply of oxygen-rich blood • The left and right coronary arteries originate at base of ascending aorta • Blood pressure here is highest in all of systemic circuit LABEL YOUR WORKSHEET Heart Failure • ~5 million Americans have heart failure & prevalence of heart failure approximately DOUBLES with each decade of life • Heart failure – – Damage to heart causes weakening of the cardiovascular system – Caused by fluid congestion or inadequate blood flow to tissues. • Heart failure may result from one or many causes – Affects circulation, lungs, neuroendocrine system & other organs – Psychological & social impacts Heart Failure Classifications • Right Heart Failure Inability of R side to adequately pump venous blood into pulmonary circulation • Left Heart Failure – Inability of L side to pump into systemic circulation • Forward Heart Failure - Inability of heart to pump blood at sufficient rate to meet O2 demands of body at rest or during exercise Heart Failure Classifications Cont…. • Backward Heart Failure Ability of heart to pump blood at sufficient rate ONLY when heart filling pressures are abnormally high. • Congestive Heart Failure Fluid in lungs or body, resulting from inadequate pumping from heart and high heart filling and venous pressures