* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrhythmia Tutorial
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
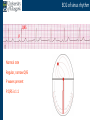
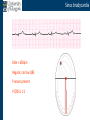
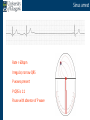
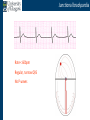
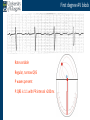
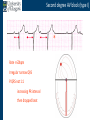
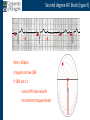
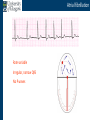
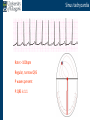
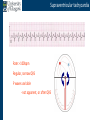
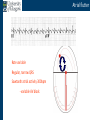
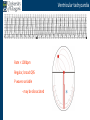
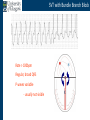
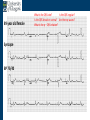
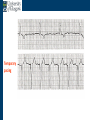
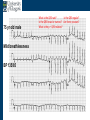
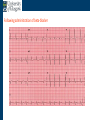
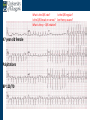
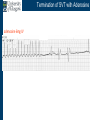
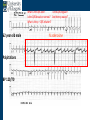
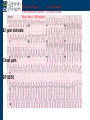
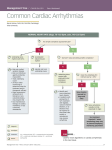
Arrhythmia recognition and treatment Cardiology Acute Care Day Objectives Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Outline Objectives Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Outline ECGofofsinus sinus rhythm ECG QRS P Normal rate Regular, narrow QRS P waves present P:QRS is 1:1 Objectives Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Outline How recognisean an arrhythmia arrhythmia How toto recognise What is the QRS rate? Are the QRS complexes regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there P waves? What is the P:QRS relation? Objectives Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Outline Bradyarrhythmias Bradyarrhythmias Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrest (“Sick Sinus Syndrome”) Junctional bradycardia Atrioventricular block (First degree) Second degree - type I (Wenckebach) / type II Third degree Sinus bradycardia Rate < 60bpm Regular, narrow QRS P waves present P:QRS is 1:1 * Sinus arrest Rate < 60bpm Irregular, narrow QRS P waves present P:QRS is 1:1 Pause with absence of P wave * Junctional bradycardia Rate < 60bpm Regular, narrow QRS No P waves * First degree AV block Rate variable Regular, narrow QRS P waves present P:QRS is 1:1 with PR interval >200ms * Second degree AV block (type I) * Rate < 60bpm Irregular narrow QRS P:QRS not 1:1 increasing PR interval then dropped beat * Second degree AV block (type II) * * Rate < 60bpm Irregular narrow QRS P:QRS not 1:1 normal PR interval with intermittent dropped beats * Third degree (complete) AV block Rate < 60bpm Regular broad QRS No relation between P and QRS * Objectives Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Outline Tachyarrhythmias Irregular Atrial fibrillation Regular Narrow QRS Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Atrial flutter Broad QRS Ventricular tachycardia SVT with Bundle Branch Block Atrial fibrillation Rate variable Irregular, narrow QRS No P waves Sinus tachycardia Rate > 100bpm Regular, narrow QRS P waves present P:QRS is 1:1 * Supraventricular tachycardias Atrial tachycardia Junctional tachycardia AV re-entrant tachycardia AV node re-entrant tachycardia * * Supraventricular tachycardia Rate > 100bpm Regular, narrow QRS P waves variable - not apparent, or after QRS * * Atrial flutter Rate variable Regular, narrow QRS Sawtooth atrial activity 300bpm - variable AV block Ventricular tachycardia Rate > 100bpm Regular, broad QRS P waves variable - may be dissociated * SVT with Bundle Branch Block * Rate > 100bpm Regular, broad QRS P waves variable - usually not visible * X Outline Normal sinus rhythm How to diagnose an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias Treatment strategy First assess the patient and CHECK THEIR PULSE Are they compromised? low BP, impaired consciousness, heart failure, chest pain Then assess the ECG Is there a high risk of cardiac arrest? VT, complete heart block If compromise or high risk Treat with electricity DC cardioversion / temporary pacing If not Look for reversible causes / treat with drugs 89 year old female Syncope BP 75/40 What is the QRS rate? Is the QRS regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there p-waves? What is the p – QRS relation? Third degree (complete) AV block Assess the patient If compromised: Immediate temporary pacing (initially transcutaneous, refer to expert to consider placing a temporary pacing wire) If not compromised: What is the risk of asystole? Third degree (complete) AV block What factors predict a high risk of asystole? - Recent asystole - Mobitz type II AV block - Third degree heart block with broad QRS - Ventricular pause >3seconds Third degree (complete) AV block What is this patients risk of asystole? High Consider temporary pacing Address reversible causes: Drugs affecting the conducting system Acute MI Temporary pacing 75 yr old male Mild breathlessness BP 135/85 What is the QRS rate? Is the QRS regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there p-waves? What is the p – QRS relation? Atrial fibrillation Assess the patient If they are compromised DC cardioversion If not, decide treatment strategy Rate control vs rhythm control Rate control AV nodal blockers CCB, β-blocker, digoxin Rhythm control Anti-arrhythmics Amiodarone, flecainide Anticoagulation Following administration of beta-blocker What is the QRS rate? Is the QRS regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there p-waves? What is the p – QRS relation? 47 year old female Palpitations BP 120/70 Supraventricular tachycardia Assess the patient If they are compromised DCCV If not compromised: Vagal manoeuvres IV Adenosine (extremely short half-life, need to give rapidly) Terminates re-entry circuits using AVN Will slow atrial tachycardia and atrial flutter IV verapamil Consider: AVN slowing (digoxin) Antiarrhythmic (amiodarone) DCCV/ A pacing Termination of SVT with Adenosine adenosine 6mg IV What is the QRS rate? Is the QRS regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there p-waves? What is the p – QRS relation? 62 year old male Palpitations BP 120/70 IV adenosine Following bisoprolol What is the QRS rate? Is the QRS regular? Is the QRS broad or narrow? Are there p-waves? What is the p – QRS relation? 82 year old male Chest pain BP 80/50 Ventricular tachycardia Assess the patient DO THEY HAVE A PULSE? No? Use BLS/ALS ALGORITHM If any compromise: Immediate DCCV Call anaesthetist Secure airway Conscious sedation Synchronised DC shock Manage on CCU If no compromise: (GET 12 LEAD ECG) Consider IV amiodarone/other antiarrhythmics Consider reversible causes Treatment strategy First assess the patient and CHECK THEIR PULSE Are they compromised? low BP, impaired consciousness, heart failure, chest pain Then assess the ECG Is there a high risk of cardiac arrest? VT, complete heart block If compromise or high risk Treat with electricity DC cardioversion / temporary pacing If not Look for reversible causes / treat with drugs Any questions Any questions? Normal sinus rhythm How to recognise an arrhythmia Bradyarrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Treatment strategy for arrhythmias