* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6-2 Solving Systems by Substituion
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
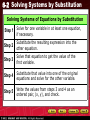
6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Preview Warm Up California Standards Lesson Presentation 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Warm Up Solve each equation for x. 1. y = x + 3 2. y = 3x – 4 x=y–3 Simplify each expression. 3. 2(x – 5) 2x – 10 4. 12 – 3(x + 1) 9 – 3x Evaluate each expression for the given value of x. 5. 2 x + 8 for x = 6 12 6. 3(x – 7) for x = 10 9 3 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution California Standards 9.0 Students solve a system of two linear equations in two variables algebraically and are able to interpret the answer graphically. Student are able to solve a system of two linear inequalities in two variables and to sketch the solution sets. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Sometimes it is difficult to identify the exact solution to a system by graphing. In this case, you can use a method called substitution. Substitution is used to reduce the system to one equation that has only one variable. Then you can solve this equation by the methods taught in Chapter 2. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution Step 1 Solve for one variable in at least one equation, if necessary. Step 2 Substitute the resulting expression into the other equation. Step 3 Solve that equation to get the value of the first variable. Step 4 Substitute that value into one of the original equations and solve for the other variable. Step 5 Write the values from steps 3 and 4 as an ordered pair, (x, y), and check. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1A: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Substitution Solve the system by substitution. y = 3x y=x–2 Step 1 y = 3x Both equations are solved for y. y=x–2 Step 2 y = x – 2 Substitute 3x for y in the second 3x = x – 2 equation. Step 3 –x –x Now solve this equation for x. 2x = –2 Subtract x from both sides and 2x = –2 then divide by 2. 2 2 x = –1 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1A Continued Solve the system by substitution. Step 4 Step 5 y = 3x y = 3(–1) y = –3 (–1, –3) Write one of the original equations. Substitute –1 for x. Write the solution as an ordered pair. Check Substitute (–1, –3) into both equations in the system. y = 3x y=x–2 –3 3(–1) –3 –1 – 2 –3 –3 –3 –3 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Helpful Hint You can substitute the value of one variable into either of the original equations to find the value of the other variable. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1B: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Substitution Solve the system by substitution. y=x+1 4x + y = 6 The first equation is solved for y. Step 1 y = x + 1 Write the second equation. Step 2 4x + y = 6 Substitute x + 1 for y in the 4x + (x + 1) = 6 second equation. 5x + 1 = 6 Simplify. Solve for x. Step 3 –1 –1 Subtract 1 from both sides. 5x = 5 5x = 5 Divide both sides by 5. 5 5 x=1 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1B Continued Solve the system by substitution. Step 4 Step 5 y=x+1 y=1+1 y=2 (1, 2) Write one of the original equations. Substitute 1 for x. Write the solution as an ordered pair. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1C: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Substitution Solve the system by substitution. x + 2y = –1 x–y=5 Step 1 x + 2y = –1 Solve the first equation for x by subtracting 2y from both sides. −2y −2y x = –2y – 1 Step 2 x – y = 5 (–2y – 1) – y = 5 –3y – 1 = 5 Substitute –2y – 1 for x in the second equation. Simplify. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 1C Continued Step 3 –3y – 1 = 5 +1 +1 –3y = 6 –3y = 6 –3 –3 y = –2 Step 4 x – y x – (–2) x+2 –2 x =5 =5 =5 –2 =3 Step 5 (3, –2) Solve for y. Add 1 to both sides. Divide both sides by –3. Write one of the original equations. Substitute –2 for y. Subtract 2 from both sides. Write the solution as an ordered pair. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1a Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. y= x+3 y = 2x + 5 Step 1 y = x + 3 y = 2x + 5 Both equations are solved for y. Step 2 y = x + 3 2x + 5 = x + 3 Substitute 2x + 5 for y in the first equation. Step 3 2x + 5 = x + 3 Solve for x. Subtract x and 5 from both sides. –x – 5 –x – 5 x = –2 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1a Continued Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. Write one of the original Step 4 y = x + 3 equations. y = –2 + 3 Substitute –2 for x. y=1 Step 5 (–2, 1) Write the solution as an ordered pair. Check Substitute (–2, 1) into both equations in the system. y=x+3 y = 2x + 5 1 2(–2) + 5 1 (–2) + 3 1 –4 + 5 1 1 1 1 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1b Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. x = 2y – 4 x + 8y = 16 The first equation is solved for x. Step 1 x = 2y – 4 Step 2 x + 8y = 16 (2y – 4) + 8y = 16 Substitute 2y – 4 for x in the second equation. Step 3 10y – 4 = 16 +4 +4 10y = 20 10y 20 = 10 10 y=2 Simplify. Then solve for y. Add 4 to both sides. Divide both sides by 10. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1b Continued Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. Step 4 x + 8y = 16 x + 8(2) = 16 x + 16 = 16 – 16 –16 x = 0 Step 5 (0, 2) Write one of the original equations. Substitute 2 for y. Simplify. Subtract 16 from both sides. Write the solution as an ordered pair. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1b Continued Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. Check Substitute (0, 2) into both equations in the system. x = 2y – 4 x + 8y = 16 0 + 8(2) 16 0 2(2) – 4 0 0 16 16 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1c Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. 2x + y = –4 x + y = –7 Step 1 x + y = –7 –y –y x = –y – 7 Step 2 x = –y – 7 2(–y – 7) + y = –4 2(–y – 7) + y = –4 –2y – 14 + y = –4 Solve the second equation for x by subtracting y from each side. Substitute –y – 7 for x in the first equation. Distribute 2. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1c Continued Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. Combine like terms. Step 3 –2y – 14 + y = –4 –y – 14 = –4 +14 +14 Add 14 to each side. –y = 10 y = –10 x + y = –7 Step 4 x + (–10) = –7 x – 10 = – 7 Write one of the original equations. Substitute –10 for y. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 1c Continued Solve the system by substitution. Check your answer. Step 5 x – 10 = –7 Add 10 to both sides. +10 +10 Step 6 x=3 (3, –10) Write the solution as an ordered pair. Check Substitute (3, –10) into both equations in the system. x + y = –7 2x + y = –4 3 + (–10) –7 –7 –7 2(3) + (–10) –4 –4 –4 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Sometimes you substitute an expression for a variable that has a coefficient. When solving for the second variable in this situation, you can use the Distributive Property. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Caution When you solve one equation for a variable, you must substitute the value or expression into the other original equation, not the one that had just been solved. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 2: Using the Distributive Property Solve y + 6x = 11 by substitution. 3x + 2y = –5 Solve the first equation for y Step 1 y + 6x = 11 by subtracting 6x from each – 6x – 6x side. y = –6x + 11 Step 2 3x + 2y = –5 Substitute –6x + 11 for y in the second equation. 3x + 2(–6x + 11) = –5 3x + 2(–6x + 11) = –5 Distribute 2 to the expression in parentheses. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 2 Continued Solve y + 6x = 11 by substitution. 3x + 2y = –5 Simplify. Solve for x. Step 3 3x + 2(–6x) + 2(11) = –5 3x – 12x + 22 = –5 –9x + 22 = –5 – 22 –22 Subtract 22 from –9x = –27 both sides. –9x = –27 Divide both sides by –9. –9 –9 x=3 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 2 Continued Solve Step 4 y + 6x = 11 by substitution. 3x + 2y = –5 y + 6x = 11 y + 6(3) = 11 y + 18 = 11 –18 –18 Write one of the original equations. Substitute 3 for x. Simplify. Subtract 18 from each side. y = –7 Step 5 (3, –7) Write the solution as an ordered pair. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 2 Solve –2x + y = 8 3x + 2y = 9 by substitution. Check your answer. Step 1 –2x + y = 8 + 2x +2x y = 2x + 8 Solve the first equation for y by adding 2x to each side. Step 2 3x + 2y = 9 3x + 2(2x + 8) = 9 Substitute 2x + 8 for y in the second equation. 3x + 2(2x + 8) = 9 Distribute 2 to the expression in parentheses. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 2 Continued Solve –2x + y = 8 3x + 2y = 9 by substitution. Check your answer. Step 3 3x + 2(2x) + 2(8) = 9 3x + 4x + 16 = 9 7x + 16 = 9 –16 –16 7x = –7 7x = –7 7 7 x = –1 Simplify. Solve for x. Subtract 16 from both sides. Divide both sides by 7. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 2 Continued Solve Step 4 –2x + y = 8 3x + 2y = 9 –2x + y = 8 –2(–1) + y = 8 y+2=8 –2 –2 y Step 5 by substitution. Check your answer. Write one of the original equations. Substitute –1 for x. Simplify. Subtract 2 from each side. =6 (–1, 6) Write the solution as an ordered pair. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 2 Continued Solve –2x + y = 8 3x + 2y = 9 by substitution. Check your answer. Check Substitute (–1, 6) into both equations in the system. 3x + 2y = 9 –2x + y = 8 3(–1) + 2(6) –3 + 12 9 9 9 9 –2(–1) + (6) 2 + (6) 8 8 8 8 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 3: Consumer Economics Application Jenna is deciding between two cell-phone plans. The first plan has a $50 sign-up fee and costs $20 per month. The second plan has a $30 sign-up fee and costs $25 per month. After how many months will the total costs be the same? What will the costs be? If Jenna has to sign a one-year contract, which plan will be cheaper? Explain. Write an equation for each option. Let t represent the total amount paid and m represent the number of months. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 3 Continued Total paid is sign-up fee plus monthly fee times months. Option 1 t = $50 + $20 m Option 2 t = $30 + $25 m Step 1 t = 50 + 20m t = 30 + 25m Both equations are solved for t. Substitute 50 + 20m for t in Step 2 50 + 20m = 30 + 25m the second equation. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 3 Continued Step 3 50 + 20m = 30 + 25m –20m – 20m 50 = 30 + 5m –30 –30 20 = 5m 20 = 5m 5 5 m=4 Step 4 t = 30 + 25m t = 30 + 25(4) t = 30 + 100 t = 130 Solve for m. Subtract 20m from both sides. Subtract 30 from both sides. Divide both sides by 5. Write one of the original equations. Substitute 4 for m. Simplify. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Additional Example 3 Continued Step 5 (4, 130) Write the solution as an ordered pair. In 4 months, the total cost for each option would be the same–$130. If Jenna has to sign a one-year contract, which plan will be cheaper? Explain. Option 1: t = 50 + 20(12) = 290 Option 2: t = 30 + 25(12) = 330 Jenna should choose the first plan because it costs $290 for the year and the second plan costs $330. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 3 One cable television provider has a $60 setup fee and $80 per month, and the second has a $160 equipment fee and $70 per month. a. In how many months will the cost be the same? What will that cost be. Write an equation for each option. Let t represent the total amount paid and m represent the number of months. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 3 Continued Total paid is fee plus monthly fee times months. Option 1 t = $60 + $80 m Option 2 t = $160 + $70 m Step 1 t = 60 + 80m t = 160 + 70m Both equations are solved for t. Substitute 60 + 80m for t in Step 2 60 + 80m = 160 + 70m the second equation. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 3 Continued Step 3 60 + 80m = 160 + 70m Solve for m. Subtract –70m –70m 70m from both sides. 60 + 10m = 160 Subtract 60 from both –60 –60 sides. 10m = 100 Divide both sides by 10. 10 10 m = 10 Write one of the original Step 4 t = 160 + 70m equations. t = 160 + 70(10) Substitute 10 for m. t = 160 + 700 Simplify. t = 860 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Check It Out! Example 3 Continued Step 5 (10, 860) Write the solution as an ordered pair. In 10 months, the total cost for each option would be the same–$860. b. If you plan to move in 6 months, which is the cheaper option? Explain. Option 1: t = 60 + 80(6) = 540 Option 2: t = 160 + 270(6) = 580 The first option is cheaper for the first six months. 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Lesson Quiz: Part I Solve each system by substitution. 1. 2. 3. y = 2x (–2, –4) x = 6y – 11 3x – 2y = –1 –3x + y = –1 x–y=4 (1, 2) 6-2 Solving Systems by Substitution Lesson Quiz: Part II 4. Plumber A charges $60 an hour. Plumber B charges $40 to visit your home plus $55 for each hour. For how many hours will the total cost for each plumber be the same? How much will that cost be? If a customer thinks they will need a plumber for 5 hours, which plumber should the customer hire? Explain. 8 hours; $480; plumber A: plumber A is cheaper for less than 8 hours.