* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Computational phylogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Corecursion wikipedia , lookup
Genetic algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Knapsack problem wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Simplex algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Travelling salesman problem wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Backtracking
Eight queens problem
1 try all possible C64 8 = 4,426,165,368
2 never put more than one queen on a
given row,
vector representation : each row specify
which column (3,1,6,2,8,6,4,7)
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
1
1
8
2
3 4 5
6 7
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
(3,1,6,2,8,6,4,7)
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
2
Queen1
for i1 = 1 to 8 do
for i2 = 1 to 8 do
....
for i3 = 1 to 8 do
sol = [i1, i2, . . . i8 ]
if solution ( sol ) then write sol stop
write “there is no solution”
Num. Of positions = 8 8 = 16,777,216
(first soln after 1,299,852
)
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
3
3 Never put queen on the same row
(different numbers on soln vector)
Queen2
sol = initial-permutation
while sol != final-permutation and not solution(sol)
do
sol = next-permutation
if solution(sol) then write sol
else write “there is no solution”
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
4
Permutation
T[1 . . n] is a global array initialize to [1,2,. . n]
initial call perm(1)
Perm(i)
if i = n then use T
else for j = i to n do exchange T[i] and T[j]
perm(i+1)
exchange T[i] and T[j]
Number of positions 8! = 40,320 (first soln after 2830)
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
5
8-queen as tree search
a vector V[1. .k] of integers between 1 and 8 is
k-promising, if none of the k queens threatens
any of the others.
A vector V is k-promising if, for every pair of
integers i and j between 1 and k with i != j, we
have V[i] - V[j] is-not-in {i-j, 0, j-i}.
Solutions to the 8-queen correspond to vectors
that are 8-promising.
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
6
Let N be the set of k-promising vectors, k: 0 .. 8.
Let G = (N,A) be the directed graph such that
(U,V) is-in A iff there exists an integer k, k:0..8 ,
such that
k=0
•U is k-promising
•V is (k+1)-promising, and
•U[i] = V[i] for every i in [1..k]
Number of node < 8!
...
k=8
(node 2057, first soln after 114 )
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
7
General Template for backtracking
Backtrack ( v[1..k] )
// v is k-promising vector
if solution ( v ) then write v
else for each (k+1)-promising vector w
such that w[1..k] = v[1..k]
do backtrack( w[1.. k+1] )
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
8
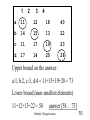
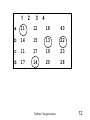
Branch and bound
The assignment problem, n agents are to be
assigned n tasks, each agent having exactly
one task. If agent i, i:1..n, is assigned task j,
j: 1..n, then the cost of performing this task is
cij. Given the cost matrix, the problem is to
assign agents to tasks so as to minimize the
total cost of executing the n tasks.
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
9
1
2
3
4
a
11
12
18
40
b
14
15
13
22
c
11
17
19
23
d
17
14
20
28
Upper bound on the answer :
a:1, b:2, c:3, d:4 = 11+15+19+28 = 73
Lower bound (sum smallest elements)
11+12+13+22 = 58
answer [58 . . 73]
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
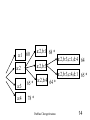
10
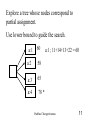
Explore a tree whose nodes correspond to
partial assignment.
Use lower bound to guide the search.
a:1
60
a:2
58
a:3
65
a:4
78 *
a:1 ; 11+14+13+22 = 60
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
11
1
2
3
4
a
11
12
18
40
b
14
15
13
22
c
11
17
19
23
d
17
14
20
28
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
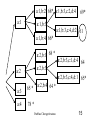
12
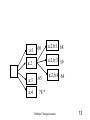
a:1
60
a:2,b:1 68
a:2,b:3 59
a:2
a:3
65
a:4
78 *
a:2,b:4 64
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
13
a:1
60
a:2,b:1 68 *
a:2,b:3
a:2
a:3
65 *
a:4
78 *
a:2,b:4 64 *
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
a:2,b:3,c:1,d:4 64
a:2,b:3,c:4,d:1 65 *
14
a:1,b:2 68* a:1,b:3,c:2,d:4
a:1
a:1,b:3
69*
a:1,b:3,c:4,d:2 61
a:1,b:4 66*
a:2,b:1 68 *
a:2,b:3,c:1,d:4 64
a:2,b:3
a:2
a:2,b:3,c:4,d:1 65*
a:3
65 *
a:4
78 *
a:2,b:4 64 *
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
15
Knapsack problem
n
max xi vi
i 1
n
xw
i 1
i
i
W
vi vi 1
wi wi 1
Suppose the variables are numbered
k
if
x1 ,..., xk
are fixed, with
xw
i 1
Adding further items
i
i
W
k
vk 1
xi vi W xi wi
i 1
i 1
wk 1
k
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
16
Heuristic search
Game tree, Artificial Intelligence
•Minimax
•A*
•Beam search
Heuristic function
Prabhas Chongstitvatana
17