* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computer Maintenance
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
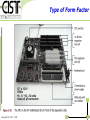
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Computer Maintenance CompTIA A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC By: JEAN ANDREW Chapter 3: Power supplies and Form Factors Objectives After you have completed this lesson, you will be able to: • Identify different kinds of power supply, computer case, and form factor • Describe how electricity is measure • Protect your computer system against damaging changes in electrical power • Describe Energy Star specifications • Install power supply & troubleshoot electrical problem Copyright © 2007 - CIST 2 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 3 Computer Case, Motherboard and Power Supply • Form Factor describes the size, shape, and major features of a hardware component. • The Form Factor of motherboard, power supply, and case must all match • Using a matching form factor for the mother board, power supply, and case assures you that: – – – – The motherboard fit in the case The power supply cords and voltage match to the board The holes in motherboard align with the hole in the case Holes in the case align with port coming of the motherboard – For some form factors, wires for switches and lights on the front of the case match up with connection on the board Copyright © 2007 - CIST 4 Computer Case, Motherboard and Power Supply A computer case is also known as a chassis Copyright © 2007 - CIST 5 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 6 Type of Form Factor • Different form factors apply to power supplies, cases, and motherboards: – – – – – – BTX ATX LPX NLX Backplane systems AT form factor (outdated) • The most common form factor: ATX, MicroATX, BTX, and NLX • The most popular form factor is ATX • BTX is the latest Copyright © 2007 - CIST 7 Type of Form Factor 12” x 13.8 “ 1980s +5, -5, +12, -12 volts Uses p8, p9 connector Copyright © 2007 - CIST 8 Type of Form Factor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 9 Type of Form Factor 12” x 9.6” most common by Intel 1995 better arrange reduce EMI installing simpler CPU beside expansion slot blow air out of case use P1 connector Soft switch or soft power Copyright © 2007 - CIST 10 Type of Form Factor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 11 Type of Form Factor • MicroATX Form Factor – Reduce total cost of a system by reducing: I/O slots on the motherboard Power supply to the motherboard Allowing for a smaller case size • BTX (Balanced Technology Extended) Form Factor – – – – Flexible and can be use by large to small system Support ATA, USB 2.0, and PCI Express technologies Reducing heat with better air flow, improve fan and cooler Use 24-pin power connector • LPX and Mini-LPX Form Factors – Develop by Western Digital – Use small case call low-Profile cases and slimline cases – Has only one expansion slot with a riser card mounted Copyright © 2007 - CIST 12 Type of Form Factor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 13 Type of Form Factor • NLX Form Factor – – – – For low-end personal computer motherboard Developed by Intel in 1998 to improve old LPX The riser card is on the edge of the board Designed to use ATX power supplies • Backplane Systems – Do not use a true motherboard – Active Backplane: no circuit other than connectors and some buffer and driver circuits – Passive backplanes: contain no circuitry at all Copyright © 2007 - CIST 14 Type of Form Factor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 15 Type of Form Factor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 16 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 17 Type of Cases • Desktop Cases – Classic case with four drives bay and around six expansion slots – A monitor is stand on the case – The motherboard sits on the bottom of the case with power supply at the back Copyright © 2007 - CIST 18 Type of Cases • Tower Cases – – – – Can be as high as two feet and has several room drives Often used for servers, and good for PC users for upgrade Provide maximum space for working inside The variations in case are as follows: Midsize towers, also called miditowers are the most popular Have around 6 expansion slots and 4 hard drives bays Used for ATX, Mini-ATX, and BTX systems • Minitower (Microtower) – Is the smallest type of tower case, no room for expansion • Full-size towers – Used for high-end personal computers and servers – Build for ATX, Mini-ATX, and BTX system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 19 Type of Cases Copyright © 2007 - CIST 20 Type of Cases • Notebook case – Are used for portable computers – Conserve space, allow portability, use less power, produce less heat Manufacturer Web site Asus www.asus.com Axxion Group Coperation www.axxion.com Enlight Corporation www.enlightcorp.com Maxpoint Computers www.enermaxusa.com MGE Company www.mgecompany.com PC Power and Cooling www.pcpowerandcooling.com PCI Case Group www.pcicase.co.uk Sunus Suntek www.suntekgroug.com Table 4-1 Manufacturers of cases and power supplies for personal computers Copyright © 2007 - CIST 21 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 22 Measures and Properties of Eelectricity Copyright © 2007 - CIST 23 Power supplies and Form Factors AC and DC • AC (alternating current): goes back and forth • DC (direct current): travel in only one direction – Rectifier: is a device that converts AC to DC – Transformer: is a device that changes the ratio of current to voltage Copyright © 2007 - CIST 24 Some Common Electronic Components Copyright © 2007 - CIST 25 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 26 Protecting Your Computer System • Static Electricity (or ESD) – Is the phenomenon that can damage component when you touch these components. To protect ESD use: Ground bracelet or static strap Ground mats Static shielding bags • EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) – Is cause by magnetic field produced as a side effect when electricity flows • Surge Protection and Battery Backup (UPS) – Surge Suppressors (surge protector) – Power Conditioner – Uninterruptible Power Supply Copyright © 2007 - CIST 27 Protecting Your Computer System Copyright © 2007 - CIST 28 Protecting Your Computer System Copyright © 2007 - CIST 29 Protecting Your Computer System • What to consider when buying a UPS Copyright © 2007 - CIST 30 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 31 Energy Star Systems (The Green Star) • Also called Green Standards: – A computer or devices that conforms to these standards can go into sleep or doze mode when not in use, thus saving energy and helping the environment. • Power-management method and features – – – – ACPI (Advance Configuration and Power Interface) APM (Advanced Power Management) AT Attachment (ATA) Display Power Management Signaling (DPMS) • Energy Star Monitor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 32 Energy Star Systems (The Green Star) Copyright © 2007 - CIST 33 Scenario In this chapter, you will learn: – Computer case, Motherboard, and Power Supply Form Factor – Type of Form Factor – Types of cases – Measures and properties of electricity – Protect your computer system – Energy Star system – Troubleshooting the electrical system Copyright © 2007 - CIST 34 Troubleshooting the Electrical System • Possible symptoms of a problem with the electrical system are: – The PC appears “dead”—no lights, no spinning drive or fan – The PC sometimes halts during boots. After several tries, it boots successfully. – Error codes or beeps occur during booting, but they come and go. – You smell burnt parts or odors. (Definitely not a good sign!) Copyright © 2007 - CIST 35 Troubleshooting the Electrical System • Check the simple things firs. Try these things: – Is everything connected and turned on? Are any cable connections loose? Is the computer plugged in? – Are all the switches turn on? – If the fan is not running, turn off the computer, open the case (Check connection of cable, are all card securely seat) – If you smell burnt parts, turn off the system and carefully search for the source of the problem Copyright © 2007 - CIST 36 Troubleshooting the Electrical System • Problems with external power • Problem with loose internal connections • Problem that come and go • Problem with an inadequate power supply • Problem with the power supply, boards, or drives • Problem with the power supply fan • Problem with the mother board • Problem with overheating • Replacing the power supply Copyright © 2007 - CIST 37 Summary active backplane electromagnetic interference (EMI) passive backplane alternating current (AC) Energy Star Power conditioners AT field replaceable unit (FRU) rectifier ATX Flex ATX resistor Baby AT Form factor sags backplane system full AT sleep mode BTX (Balance Technology Extended) Green Standard slimline case bus riser intelligent UPS smart UPS capacitor LPX surge suppressor diode Micro-ATX tower case direct current (DC) Mini-LPX transformer desktop case NLX transistor Copyright © 2007 - CIST 38 Summary • Form Factor is a set of specifications for the size and configuration of hardware components, such as case power supplies and mother boards. • The most common form factor is ATX. The other like AT, Baby AT, BTX, LPX and NLX, Backplane System. • Case type include desktop, low-profile or slimline desktop, minitower, miditower, full-size tower and notebook. Miditower is the most popular today. • Microcomputer requires Direct Current, which convert from AC (Alternating Current). Copyright © 2007 - CIST 39 Summary • A power supply is actually a transformer and rectifier, rather than a supplier of power. • A transistor is a gate or switch for an electrical signal, a capacitor holds an electrical charge, a diode allow electricity to flow in one direction, and a resistor limits electrical current. • To protect a computer against ESD, use a ground bracelet, ground mat, and static shielding bags. • Device that control the electricity to a computer include surge suppressors, line conditioner, and UPS. Copyright © 2007 - CIST 40 Power supplies and Form Factors QUIZ – choose the correct answer • How many kind of UPS are there? -1 -3 -2 -4 • Line conditioner level the AC to reduce - brownout - spikes - power - voltage • A faulty power supply can cause: - Memory error - data errors - system hangs - reboot - it can damage a mother board or other components • Device that are Energy Star-compliant go into sleep mode, in which they use less than - 35 watts of power Copyright © 2007 - CIST - 30 watts of power 41 Question Questions? Video ‘chapter 3/Replacing the power supply’ and now it’s time to practice Copyright © 2007 - CIST 42