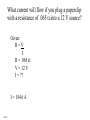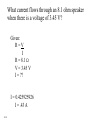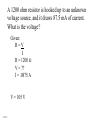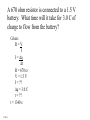* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01-02MurraysOhmsLaw
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
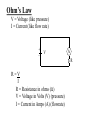
Ohm’s Law •Definition •Whiteboards •An Elaborate Analogy Ohm’s Law V = Voltage (like pressure) I = Current (like flow rate) + - V A R R=V I R = Resistance in ohms () V = Voltage in Volts (V) (pressure) I = Current in Amps (A) (flowrate) Ohm’s Law - The way I think of it V = Voltage (like pressure) I = Current (like flowrate) R = Resistance to flow + - V I=V R R = Resistance in ohms () V = Voltage in Volts (V) (pressure) I = Current in Amps (A) (flowrate) A R Ohm’s Law I= + - V R R = Resistance in ohms () V = Voltage in Volts (V) (pressure) I = Current in Amps (A) (flowrate) Demo - pass around resistors (two properties - power and resistance) Demo - power supply, resistor, light bulb (show increase/decrease V, and R) A V R Black Brown Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet Gray White Gold Silver No color 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 5% 10% 20% Ohm’s Law + - 12.0 V A R=V I R = Resistance in ohms () V = Voltage in Volts (V) (pressure) I = Current in Amps (A) (flowrate) 120. mA R= ?? Example 1: What is the resistance in the circuit above? R = V/I = (12.0 V)/(.120 A) = 100. Example 2: If there is a 220 resistor in the circuit above, what is the current? R = V/I, I = V/R = (12.0 V)/(220 ) = .05454 = .055 A or 55 mA Whiteboards 1|2|3|4|5|6 What is the resistance of a light bulb if it draws 250 mA of current from a 6.15 V battery? (1000 mA = 1 A) Given: R=V I R = ?? V = 6.15 V I = .250 A R = 24.6 24.6 What current will flow if you plug a paperclip with a resistance of .065 into a 12 V source? Given: R=V I R = .065 V = 12 V I = ?? I = 184.6 A 180 A What voltage do you need to push 1.5 Amps of current through a 210 ohm resistor? Given: R=V I R = 210 V = ?? I = 1.5 A V = 315 V 315 V What current flows through an 8.1 ohm speaker when there is a voltage of 3.45 V? Given: R=V I R = 8.1 V = 3.45 V I = ?? I = 0.425925926 I = .43 A .43 A An unknown resistor draws .0128 Amps of current from a 23.9 V source. What is the resistance? Given: R=V I R = ?? V = 23.9 V I = .0128 R = 1867.1875 R = 1870 1870 A 1200 ohm resistor is hooked up to an unknown voltage source, and it draws 87.5 mA of current. What is the voltage? Given: R=V I R = 1200 V = ?? I = .0875 A V = 105 V 105 V A 670 ohm resistor is connected to a 1.5 V battery. What time will it take for 3.0 C of charge to flow from the battery? Given: R=V I I = q t R = 670 V = 1.5 V I = ?? q = 3.0 C t = ?? t = 1340 s 1340 s A 3.0 V battery with a capacity of 350 mAh (350 milli amp hours) is drained in 4 hours and 27 minutes. What is the resistance of the circuit that it is attached to? Given: R=V I I = q t R = ?? V = 3.0 V I = ?? q = (.350e-3)(3600) = 1260 C t = 4*3600 + 27*60 = 16020 s R = 38.14286 = 38 38 Symbols + - A Cell. + and -, Infinite current, R = 0, what’s really inside A Battery of cells A resistor V3 A voltmeter, R = infinity A3 An ammeter, R = 0 An analogy Water in pipes: Flow rate (GPM) Pressure Constriction Constant P Pump Electrons in wires: Current (Amps = C/s) Voltage Resistance Batteries/Cells R1 + - A3 R2 Current convention Restriction Wires are superconductors