* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sample Presentation Title
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
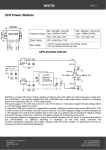
Brake Intensity Advisory System Final Design Assessment Jace Hall Michael Purvis Caleb Trotter Edward Yri ECE 4007-L01 12/05/2011 Project Details • What - BIAS (Brake Intensity Advisory System) operates by illuminating an auxiliary set of LEDS located around the perimeter of the standard brake lights when “hard braking” occurs • Cost - The cost associated with mass production of the BIAS is projected to be $66.83 2 Project Motivation • Why - The percentage of rear-end collisions (17% of all claims) ranks second among all automobile accidents • Who - BIAS is intended for drivers and car manufacturers who are concerned with operating and manufacturing safer vehicles 3 Proposed vs. Actual Design Goals Proposed Design Goal Simple integration with current braking systems Non-intrusive design Real-time response Software definability based on vehicle brake force parameters 4 Actual Design Feature Design Goal Achieved Design Goal Achieved Design Goal Achieved Design Goal Achieved Proposed vs. Actual Technical Objectives Proposed Technical Objectives 5 Actual Technical Performance Receive a voltage sensor output between 0-3.3 V corresponding to a defined force. Tech. Objective Achieved Categorize the inputs into three defined states using the Mbed microcontroller. Tech. Objective Achieved Illuminate the auxiliary LEDs when a voltage of 1.9V or higher is received by the microcontroller. Tech. Objective Achieved Achieve a visual indication of braking force in real time. Tech. Objective Achieved High Level BIAS Schematic 6 Implemented BIAS Design 7 BIAS Operation 8 Testing the Force Sensing Resistor Circuitry Output Specification •0 – 3.3 V output from the force sensing resistor circuit Testing Method •The FSR was attached to the vehicle brake pedal, and the divider circuit resistor was sized to produce the appropriate output 9 Confirming Transition at the Hard Breaking Voltage Threshold Specification • Real time response to the determined voltage threshold value Testing Method • A volt meter measured the FSR voltage when the second LED array zone was initially illuminated. The value was 1.9 volts 10 Software Tests Specifications • Three defined controller states corresponding to illumination parameters • Software definability Testing Method • LED output confirmed the controller states operated properly • Sensitivity was altered to ensure software definability 11 Design Modifications • 12 V voltage regulator added to reduce 13.8 V car outlet voltage • 1.5 MΩ grounding resistor added to LED driver circuit • Common grounding network established 12 Supporting Design Modification Figure 13 Problems Encountered and Solutions • Problem: The LED driver circuit current limiting resistors were overloaded • Solution: New resistors were added with higher power ratings • Problem: LED brightness was not consistent • Solution: Shorted soldering points were located, and fixed 14 Prototype Cost Analysis • Prototype Expenditures - Of the requested $405, $128.97 was spent - Many of the required parts were donated • Mass Production Cost - Reduced hardware cost based on quantities purchased - Lower microcontroller cost based on reduction of features 15 Production Cost Break Down Parts Mass Production Cost Prototype Cost FSR $16.00 $7.95 Wire/Connectors $5.50 Donated Resistors/Voltage Regulator/Capacitors $4.95 Donated Perforated Boards $5.75 Donated Microcontroller $2.16 Donated ($60) LEDs $19.25 $19.25 LED Drivers $4.50 $4.50 Parts Total $58.11 $31.70 ($91.70) Contingency (15%) $8.72 $4.76 ($13.76) $66.83 $36.46 ($105.46) TOTAL 16 Marketability and Projected Profits – No automobile manufactures currently use a FSR to process braking force and illuminate brake lights accordingly – Profits from the system would come from royalty payments allotted to the patent holders Projected BIAS Royalty Profits Payment per Unit Installed Projected Installations Total Profits $2.00 500,000 $1,000,000 * Projected installations based on ~25% of the vehicles produced by Ford Motor Company annually 17 Improvements and Future Work • Create a printed circuit board for control and FSR circuitry • Integrate and program a lower cost microcontroller • Fabricate lenses to cover LED arrays • Test BIAS system on alternative vehicles 18