* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
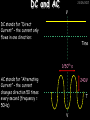
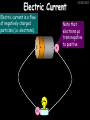
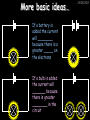
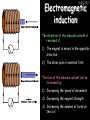
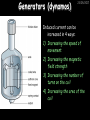
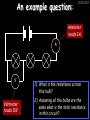
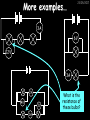
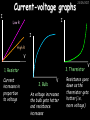
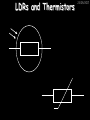
23/05/2017 Producing and Measuring Electricity Edexcel W Richards The Weald School DC and AC 23/05/2017 V DC stands for “Direct Current” – the current only flows in one direction: Time 1/50th s AC stands for “Alternating Current” – the current changes direction 50 times every second (frequency = 50Hz) 240V T V Types of Batteries Type of Battery Contains Uses Wet cell rechargeable Lead and acid Cars, industry Dry cell rechargeable Nickel, cadmium, lithium Mobile phones, power tools Dry cell nonrechargeable Zinc, carbon, manganese, lithium Torches, clocks, hearing aids 23/05/2017 Why use rechargeable batteries? Why use standard batteries? • Long long-term expense • No need for charger • Can be used many times • Less expensive • Less energy to produce • Rechargeables contain carcinogens Battery Capacity 23/05/2017 The capacity of a battery is measured in Amp Hours (Ah). Basically, a battery with a capacity of 1Ah will provide a current of 1A for 1 hour. Capacity (Ah) = Current (A) x Time (hours) 1) A battery provides a current of 2A for 2 hours. What was its capacity? 2) Another battery has a capacity of 10Ah. If it runs out after half an hour what current was being drawn? 3) A mobile phone battery has a capacity of 1100mAh. If it runs on a current of 250mA when being used in a phone call how long could the call last? Electric Current Electric current is a flow of negatively charged particles (i.e. electrons). + e- - e- 23/05/2017 Note that electrons go from negative to positive Basic ideas… 23/05/2017 Electric current is when electrons start to flow around a circuit. We use an _________ to measure it and it is measured in ____. Potential difference (also called _______) is how big the push on the electrons is. We use a ________ to measure it and it is measured in ______, a unit named after Volta. Resistance is anything that resists an electric current. It is measured in _____. It usually increases when a device gets hot. Words: volts, amps, ohms, voltage, ammeter, voltmeter More basic ideas… If a battery is added the current will ________ because there is a greater _____ on the electrons If a bulb is added the current will _______ because there is greater ________ in the circuit 23/05/2017 23/05/2017 Electromagnetic induction The direction of the induced current is reversed if… 1) The magnet is moved in the opposite direction 2) The other pole is inserted first The size of the induced current can be increased by: 1) Increasing the speed of movement 2) Increasing the magnet strength 3) Increasing the number of turns on the coil Generators (dynamos) 23/05/2017 Induced current can be increased in 4 ways: 1) Increasing the speed of movement 2) Increasing the magnetic field strength 3) Increasing the number of turns on the coil 4) Increasing the area of the coil Resistance 23/05/2017 Resistance is anything that will RESIST a current. It is measured in Ohms, a unit named after me. Georg Simon Ohm 1789-1854 The resistance of a component can be calculated using Ohm’s Law: Resistance (in ) = V Voltage (in V) Current (in A) I R An example question: 23/05/2017 Ammeter reads 2A A V Voltmeter reads 10V 1) What is the resistance across this bulb? 2) Assuming all the bulbs are the same what is the total resistance in this circuit? More examples… 23/05/2017 3A 6V 12V 3A 2A 4V 2V 1A What is the resistance of these bulbs? Resistance 23/05/2017 Resistance is anything that opposes an electric current. Resistance (Ohms, ) = Potential Difference (volts, V) Current (amps, A) What is the resistance of the following: 1) A bulb with a voltage of 3V and a current of 1A. 2) A resistor with a voltage of 12V and a current of 3A 3) A diode with a voltage of 240V and a current of 40A 4) A thermistor with a current of 0.5A and a voltage of 10V Current-voltage graphs I 23/05/2017 I Low R I High R V 3. Thermistor 1. Resistor Current increases in proportion to voltage 2. Bulb V As voltage increases the bulb gets hotter and resistance increases V Resistance goes down as the thermistor gets hotter (i.e. more voltage) LDRs and Thermistors 23/05/2017 LDRs and Thermistors 1) Light dependant resistor – resistance DECREASES when light intensity INCREASES Resistance 23/05/2017 2) Thermistor – resistance DECREASES when temperature INCREASES Resistance Amount of light Temperature Electrical Inventions Match these inventions with when they were invented: Electric kettle 1876 Telephone 1882 Television 1891 Electric fire 1892 Electric iron 1908 Vacuum cleaner 1920s 23/05/2017 Computers 23/05/2017 Apple 1 (1976) – 1Mhz IBM 5100 portable PC (1975), 25kg, processor, 4K RAM, cost $670 1.9MHz processor, 64K RAM, 200K internal tape storage, cost up to $20,000 Commodore 64 (1982) – 1Mhz processor, 64K RAM, 16 colours, cost $600, 17m sold Apple Macintosh (1984) – 8Mhz processor, 512K RAM, cost $2500 Superconductivity 23/05/2017 In 1911 I discovered superconductivity. This is when a metal can conduct electricity with zero resistance. I won the Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1913. Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (1853-1926) The Maglev train is based on superconductivity and uses magnets to propel the train to speeds of over 300mph.