* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ohm’s Law and Electrical Power
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
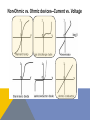
OHM’S LAW “Provided the physical conditions, such as temperature, are kept constant, the resistance is constant over a wide range of applied potential differences, and therefore the potential difference is directly proportional to the current flowing.” 𝑽 = 𝑰𝑹 OHMIC DEVICES (OHMIC CONDUCTORS) • Those devices which obey the linear relationship of Ohm’s Law at all potential differences • Temperature of this device will NOT change due to the heating effect of the current as voltage changes • No device is truly completely Ohmic—it’s an ideal resistor •Most devices would be considered Non-Ohmic Non-Ohmic vs. Ohmic devices—Current vs. Voltage