* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Application of photodiodes - Oklahoma State University
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
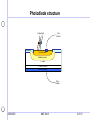
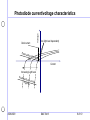
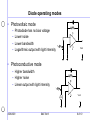
Application of photodiodes A brief overview 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 1 of 10 Quantum devices • Absorption of a photon of sufficient energy elevates an electron into the conduction band and leaves a hole in the valence band. • Conductivity of semi-conductor is increased. • Current flow in the semi-conductor is induced. Conduction band - Electron Energy gap Energy level + Hole Valence band Photon (hv) 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 2 of 10 Photodiode structure Incident light Front Contact Insulation p+ Active Area Depletion region n- region n+ Back Diffusion Back Metalization Rear Contact 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 3 of 10 Photodiode fundamentals • Based on PN or PIN junction diode – photon absorption in the depletion region induces current flow P + hole h I IL electron N • Spectral sensitivity Material Band gap (eV) Spectral sensitivity silicon (Si) 1.12 250 to 1100 nm indium arsenide (InGaAs) ~0.35 1000 to 2200 nm Germanium (Ge) .67 900 to 1600 nm 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 4 of 10 RL Photodiode characteristics • Circuit model – I0 Dark current (thermal) – Ip Photon flux related current Rs Ip I0 Rj Cj • Noise characterization – Shot noise (signal current related) – q = 1.602 x 10–19 coulombs – I = bias (or signal) current (A) – is = noise current (A rms) is 2qi – Johnson noise (Temperature related) – – – – – 3/26/2003 k = Boltzman’s constant = 1.38 x 10–23 J/K T = temperature (°K) B = noise bandwidth (Hz) R = feedback resistor (W) out eOUT = noise voltage (Vrms) e BAE 5413 4kTBR 5 of 10 Dark current Photovo Voltage Photodiode current/voltage characteristics Isc (light level dependent) ltaic mo de load line Current Increasing Light level Photoco nductiv e load lin mode e 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 6 of 10 Trans-impedance amplifier function • Current to voltage converter (amplifier) • Does not bias the photodiode with a voltage as current flows from the photodiode (V1 = 0) • Circuit analysis Io 0 V + I f I s f V1 0 V f R f I f R f I s V1 Is Io - - + + If Vout Vout V f R f I s –Note: current to voltage conversion 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 7 of 10 Diode operating modes • Photovoltaic mode – – – – Photodiode has no bias voltage Lower noise Lower bandwidth Logarithmic output with light intensity + + Vout • Photoconductive mode – Higher bandwidth – Higher noise – Linear output with light intensity + Vs 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 + Vout 8 of 10 For the photovoltaic mode • I = thermal component + photon flux related current eV heP kT I I 0 e 1 h • where I = photodiode current V = photodiode voltage I0 = reverse saturation current of diode e = electron charge k = Boltzman's constant T = temperature (K) = frequency of light h = Plank’s constant P = optical power h = probability that hv will elevate an electron across the band gap 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 9 of 10 Circuit Optimization • Burr-Brown recommendations (TI) • Photodiode capacitance should be as low as possible. • Photodiode active area should be as small as possible so that CJ is small and RJ is high. • Photodiode shunt resistance (RJ ) should be as high as possible. • For highest sensitivity use the photodiode in a “photovoltaic mode”. • Use as large a feedback resistor as possible (consistent with bandwidth requirements) to minimize noise. • Shield the photodetector circuit in a metal housing. • A small capacitor across RF is frequently required to suppress oscillation or gain peaking. • A low bias current op amp is needed to achieve highest sensitivity 3/26/2003 BAE 5413 10 of 10