* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Zener Diode
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
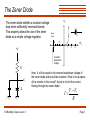
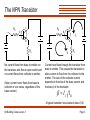
The Zener Diode The zener diode exhibits a constant voltage drop when sufficiently reversed-biased. This property allows the use of the zener diode as a simple voltage regulator. +IF zener point -6 -3 +VF 1 +V 2 3 Constant breakdown voltage R Vr D Kit Building Class Lesson 3 Here, Vr will be equal to the reverse breakdown voltage of the zener diode and should be constant. What is the purpose of the resistor in this circuit? Its job is to limit the current flowing through the zener diode: V Vr I R Page 1 The Bipolar Junction Transistor The transistor is a versatile device usually configured to perform as a switch or as an amplifier. The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is the most common type and has three leads: 3 Base 3 Collector 2 Base 1 Emitter PNP Transistor Collector 2 1 Emitter NPN Transistor In a transistor, the flow of current from the collector to the emitter is controlled by the amount of current flowing into the base of the transistor. If no current flows into the base, no current will flow from the collector to the emitter (it acts like an open switch). If current flows into the base, then a proportional amount of current flows from the collector to the emitter (somewhat like a closed switch). Kit Building Class Lesson 3 Page 2 The NPN Transistor Rb + c Rb b + c b IC + e e - Re No current flows from base to emitter, so the transistor acts like an open switch and no current flows from collector to emitter. (Note: current never flows from base to collector or vice versa, regardless of the base current.) + - IB Re Current now flows through the transistor from base to emitter. This causes the transistor to allow current to flow from the collector to the emitter. The size of the collector current depends on the size of the base current and the beta b of the transistor: b IC I B A typical transistor has a beta of about 100. Kit Building Class Lesson 3 Page 3 Base and Collector Currents What’s the base current IB? Use Kirchhoff’s voltage law: c RB b IC E I B RB I B RE 0.7V Now find the collector current IC: IC b I B Kit Building Class Lesson 3 E e E I B ( RB RE ) 0.7V E 0.7V IB RB RE + - 0.7 volts is lost at the junction of the base and emitter IB RE What’s the maximum value for the collector current? E IC RE Page 4 The PNP Transistor c b Ib Ic - Rb e + Re The PNP transistor behaves identically to the NPN transistor, except that all polarities are reversed. The voltages are applied with opposite polarity, and the currents run opposite to those in the NPN transistor, but all other behaviors are the same. Kit Building Class Lesson 3 Page 5