* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World History: The Rise of Medieval Europe
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
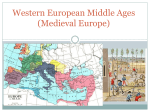
World History: The Rise of Medieval Europe Ms Shari Rise of Medieval Europe Frankish Rulers - strongest Germanic group Settled in France and Germany A.D. 700 King of the Franks - Clovis (Adopted Catholicism) Mayors of the Palaces - Frankish Government officials who had real power given to them by the king. Charles Martel was a Mayor of a Palace who defeated Muslims and defended France. Son of Charles - Pepin the Short Pepin forced Lombards out and gave land to Church. Annointed by Pope and secured tie to Church. Pepin’s son - Charlemagne or Charles the Great. Charles the Great Charlemagne’s Empire included Germany, France, Northern Spain and Italy. Defended Pope Leo III against Roman Nobles Pope Crowned Charles the new Roman Emperor. Set up Capital in Germany Greatest Frankish ruler Charles died and his 3 grandsons split his empire (Germany, Italy, France) Signed Treaty of Verdun A.D. 843 to settle the split A New Europe The grandsons lost land to invaders Vikings/Norseman, Muslims, Slavs, Nomads Isolated communities and weakened Central Governments, trade declined, economic collapse. Nobles and non royals back in power A.D. 800 - new political system began Feudalism Feudalism An exchange of goods and services for protection of lands and people. Land given to nobles in exchange for loyalty and military help. Nobles obligated to provide Knights (mounted warriors) to the royal army. (Bullies and thugs) Code of Knights was Chivalry Age 7 live with nobleman; Age 15 a Squire could train as a Knight. Warriors granted Fiefs or estates with peasants Later fiefs granted to counts and local officials. System of Feudalism ∆ Like a pyramid King Lords Vassals Knights /Squire Serfs/Peasants Life in the Feudal System Lords had almost total authority Ladies had few or any rights (house work) Entertainment was called Tournament - mock battles of military skills and hunting. Jousting, Falconry, Archery, Horseback riding Life of a Nobleman Tie between the Noble and Vassal were made official in a ceremony known as a Homage. Most important pledge was military service. Every nobleman built a castle Built on a hill, surrounded by a Moat and strongest part was the Keep. Surrounding the keep was an open area called the Bailey (many useful rooms). Manorial System System of Agricultural production Provided lords and peasants with food, shelter and protection. Economic system between Lords and Serfs. Serfs were bound to Lords, but were not slaves Could not be sold apart from the land. Peasants could gain freedom if they could run and avoid detection for 1 year and 1 day. The Medieval Church Kingdom of Christians “Christiandom or Age of Faith” Pope was the strongest political leader in Western Europe. Catholic claim - Peter the Apostle was Rome’s first Bishop, chosen by Jesus to lead the church. Believed all people were sinners dependent on God’s grace or favor. Medieval Church Continued Eucharist - Holy Communion Baptism, Penance, Confirmation, matrimony, anointing of the sick and holy orders. Mass or religious services in Latin Pope, Bishops, Priests (Secular Clergy) Friars, Monks, Nuns (Regular Clergy) lived apart from society. Roman Official Benedict founded a monastery in Italy. Benedictine Rule - poverty, chastity and obedience Abbot or head of a Monastery Nuns under rule of Abbess Church Reform Began with Monks and Friars Cardinals appointed Popes Pope has complete jurisdiction over the church Non Clergy were stopped from giving religious gifts as rewards. Heresy - crimes against church (convert Jews) Pope Innocent III was the most powerful Pope Inquisitions in A.D. 1232 Arrested for criticizing or challenging the basic teachings of the church. Tried and Excommunicated if found guilty. Later tortured and burned at the stake. Catholic Power Grew - A.D. 1200’s Jews were persecuted further. Blamed for social and economic problems Blamed for the death of Jesus Required to wear badges on their clothing Required to live in Ghettos and pay high taxes. Lost rights to own land, trade and later expelled to Poland. Christians could not live in Jewish homes or provide medical care to Jews, Actions by Christians served to remove power and position of Jewish people. “Sound Familiar” Crusades 1096 - 1272 Pope Urban II called for Christians to make a Pilgrimage to Jerusalem and capture the Holy Land from the Muslims “infidels” Those who fought were Crusaders. 9 military expeditions in all (Battles fought in Germany and France because of large populations of Jews) Most vicious battle was the Battle of Mayence in South of France. 1300 Jews invited to hide in Archbishop’s palace. Slaughtered and property distributed. 1099 Crusaders captured Jerusalem. Herded all the Jews into a synagogue as they circled it holding hands They sang “Christ we adore thee” while they burned the Jews alive. Effects of the Crusades Helped end Feudalism Increased monarchy power People had larger views of the world United all Muslim Islamics in the world Promoted Trade and Cultural Exchange Cultural and Economic improvements (new plow, collar harness, crop rotation, roads repaired and rebuilt. Fairs aided trade and cultural exchange Banking in Medieval Europe Brought the rise of money economy Money Exchangers determined values, transferred funds, deposits, and made loans. Jews and Italians were some of the 1st Bankers especially during Crusades. People came in contact and traded goods for $ Jews acted as Money exchangers Bankers $ Rise of Disease Towns grew on waterways and off roads Streets were alleyways, buildings wood and thatch roofs. Bandits made it necessary for wood/stone fences around towns. ALMOST NO SANITATION - tossed in streets Diphtheria, typhoid, flu, malaria, Bubonic Plague or BLACK DEATH. BLACK DEATH A.D. 1348 - 1350 Fleas infected the rats who then infected humans. Came on trade ships from China to Italy Spread to every corner of Europe (populated areas) Took over 30 years for Plague to end “Ring a Round the Rosie, Pocket full of posies, ashes, ashes, we all fall down” Killed over 1/3 of Europe’s Population Jews were blamed for Disease and burned alive, hanged and murdered. Accused of poisoning the wells or magic that brought the disease to the Christians. Medieval Middle Class Hospitals and medical care grew Business and Guilds monopolized trade Masters - Journeyman - Apprentices Artisans - Blacksmiths, carpenters, shoemakers, tailors, weavers, masons, maids Townspeople granted charters - gave rights to control their own affairs, and businesses Burghers in Germany, Bourgeoisie in France, Burgesses in England (Middle Class Groups) Medieval Education Nobles and rich went to universities Schools modeled after law school in Bologna, Italy and specialized in medicine and law. System of thought - Scholasticism Catholics opposed this thinking that combined learning of reason and faith. Rejected Aristotle’s and scholarly teachings as heresy. Thomas Aquinas - A.D. 1200 most important scholastic thinker (His teachings - God’s Gifts) Medieval Art and Literature Epics and Romances Songs written into stories Traveling Poet-Musicians - Troubadours or Mintrels. Late Medieval Literature written in Vernacular (everyday languages of their region) Art seen in Churches (Romanesque) French architecture (Gothic) Angleland England - Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms united Alfred the Great Defeated the Danish Vikings who earlier crossed English channel to invade England. He was the 1st to have “Great” title. French William Duke of Normandy won the English Crown in A.D. 1066 William the Conqueror - 1st Norman King New English Culture William the Conqueror’s grandson King Henry II Created Common Law, Grand and Petit Jury Sons Richard the lionhearted and John John took over when Richard left to fight in Crusades King John taxed nobles due to loss of income Nobles wrote Magna Carta to limit kings power Great Council of nobles created (Parliament) Knights enforced the Magna Carta and protected Noblemen House of Lords and House of Commons compares to our Congress (Senate and House of Representatives) Monarchy Rise to Power Hundred’s Year War - England and France battle A.D. 1337 - 1453 English fought to keep Land William the Conqueror had acquired (Northern France) A.D. 1337 England’s King Edward III claimed French Crown. Longbow gave the English victories Monarchs replaced fuedal soldiers with national armies. Joan of Arc and France 17 year old girl who made Charles VII King of France She heard her saints her instructed her to save France from the English. French beat English at Orleans, Joan was hero English kidnapped Joan Church tried her for heresy/burned at stake. France united and developed a strong centralized Government but had independent rulers in regions. Church Canonized Joan of Arc (made her a saint over 500 years later) English Monarchy War of the Roses Family members fight over Monarchy House of Lancaster (Red Rose) House of York (White Rose) Red Rose family WON! King Henry VII Tudor Monarcy won control Spanish Monarchy A.D. 1469 King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella Ferdinand of Aragon Isabella of Castile Married and ruled separate but royal power united Spain Cortes (assemblies) reviewed royal policies Moors and Jews left Spain weakening their economy (lost banker, businesses, skilled) Spanish Inquisitions made Monarchy powerful! Troubled Catholic Church Holy Roman Empire largest political unit Monarchs weakened power of Church France controlled Church Romans forced Cardinals to elect Italian Pope after death of French Pope Clement. This change was called “Great Schism”. Church Corruption was outrageous Simony - selling of church positions to wealthy Indulgences - pay for your sins to be forgiven Church Challengers - John Wickliffe and Jan Hus who was burned at the stake