* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
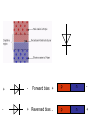
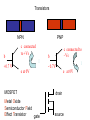
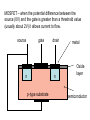
Conductors – many electrons free to move Insulators – few free electrons Semi-conductors – insulators when pure but can be made conductive by adding impurities (doping), stimulating with heat, light, or a voltage Intrinsic (pure ) semi-conductor has 4 electrons in the outer shell all form bonds unless there is a disruption to the crystal pattern. Doping p – type semiconductor n – type semiconductor + Charge carrier - electron - + Charge carrier - hole - + - Forward bias + p n - - + Reversed bias - p n + Experiment PN Junction Diode Characteristics Light emitting diodes Forward biased pn junction e + p n - When electron hole pairs recombine they give out energy E = hf If the energy is large enough the frequency of the light will be visible Photodiode – reacts very quickly to light Photovoltaic mode (forward biased) When light shines on the junction electrons are given enough energy to escape the atom forming electron hole pairs. This gives a voltage across the junction. There will be no other power source in the circuit. Used in solar cell for calculators etc. Photoconductive mode (reverse biased) When light shines on it the resistance decreases as electrons are given enough energy to escape the atom so the number of charge carriers increases. The current in the circuit will increase. Current is proportional to irradiance Transistors NPN b PNP c connected to +Vs b I +0.7 V - 0.7V e at 0V c connected to - Vs I e at 0V MOSFET drain Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor gate source MOSFET – when the potential difference between the source (0V) and the gate is greater than a threshold value (usually about 2V) it allows current to flow. source gate n p-type substrate drain n metal Oxide layer semiconductor