* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CMOS FUNDAMENTAL
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
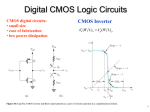
Introduction to CMOS Transistor and Transistor Fundamental Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): very many Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor – Fast, cheap, low power transistors Today: How to build your own simple CMOS chip – CMOS transistors – Building logic gates from transistors – Transistor layout and fabrication Rest of the course: How to build a good CMOS chip 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 2 Silicon Lattice Transistors are built on a silicon substrate Silicon is a Group IV material Forms crystal lattice with bonds to four neighbors 0: Introduction Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si CMOS VLSI Design Slide 3 Dopants Silicon is a semiconductor Pure silicon has no free carriers and conducts poorly Adding dopants increases the conductivity Group V: extra electron (n-type) Group III: missing electron, called hole (p-type) 0: Introduction Si Si Si Si Si Si As Si Si B Si Si Si Si Si - + + - CMOS VLSI Design Si Si Si Slide 4 p-n Junctions A junction between p-type and n-type semiconductor forms a diode. Current flows only in one direction 0: Introduction p-type n-type anode cathode CMOS VLSI Design Slide 5 nMOS Transistor Four terminals: gate, source, drain, body Gate – oxide – body stack looks like a capacitor – Gate and body are conductors – SiO2 (oxide) is a very good insulator – Called metal – oxide – semiconductor (MOS) capacitor Source Gate Drain Polysilicon – Even though gate is SiO2 no longer made of metal n+ n+ p 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design bulk Si Slide 6 nMOS Operation Body is commonly tied to ground (0 V) When the gate is at a low voltage: – P-type body is at low voltage – Source-body and drain-body diodes are OFF – No current flows, transistor is OFF Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO2 0 n+ n+ S p 0: Introduction D bulk Si CMOS VLSI Design Slide 7 nMOS Operation Cont. When the gate is at a high voltage: – Positive charge on gate of MOS capacitor – Negative charge attracted to body – Inverts a channel under gate to n-type – Now current can flow through n-type silicon from source through channel to drain, transistor is ON Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO2 1 n+ n+ S p 0: Introduction D bulk Si CMOS VLSI Design Slide 8 pMOS Transistor Similar, but doping and voltages reversed – Body tied to high voltage (VDD) – Gate low: transistor ON – Gate high: transistor OFF – Bubble indicates inverted behavior Source Gate Drain Polysilicon SiO2 p+ p+ n 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design bulk Si Slide 9 Power Supply Voltage GND = 0 V In 1980’s, VDD = 5V VDD has decreased in modern processes – High VDD would damage modern tiny transistors – Lower VDD saves power VDD = 3.3, 2.5, 1.8, 1.5, 1.2, 1.0, … 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 10 Transistors as Switches We can view MOS transistors as electrically controlled switches Voltage at gate controls path from source to drain d nMOS pMOS g=1 d d OFF g ON s s s d d d g OFF ON s 0: Introduction g=0 s CMOS VLSI Design s Slide 11 Complementary CMOS Complementary CMOS logic gates – nMOS pull-down network – pMOS pull-up network inputs – static CMOS Pull-up OFF Pull-up ON Pull-down OFF Z (float) 1 Pull-down ON X (crowbar) 0: Introduction 0 CMOS VLSI Design pMOS pull-up network output nMOS pull-down network Slide 12 Series and Parallel nMOS: 1 = ON pMOS: 0 = ON Series: both must be ON Parallel: either can be ON a a 0 g1 g2 (a) (b) a g1 g2 (c) a g1 g2 b 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design 0 1 b b OFF OFF OFF ON a a a a 0 1 1 1 0 1 b b b b ON OFF OFF OFF a a a a 0 0 b 1 b 0 b 1 1 0 g2 a b a g1 a 0 0 b (d) a 0 1 1 0 1 1 b b b b OFF ON ON ON a a a a 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 b b b b ON ON ON OFF Slide 13 CMOS Inverter A VDD Y 0 1 A A Y Y GND 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 14 CMOS Inverter A VDD Y 0 1 OFF 0 A=1 Y=0 ON A Y GND 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 15 CMOS Inverter A Y 0 1 1 0 VDD ON A=0 Y=1 OFF A Y GND 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 16 CMOS NAND Gate A B 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 Y Y A B 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 17 CMOS NAND Gate A B Y 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0: Introduction ON ON Y=1 A=0 B=0 CMOS VLSI Design OFF OFF Slide 18 CMOS NAND Gate A B Y 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0: Introduction OFF ON Y=1 A=0 B=1 CMOS VLSI Design OFF ON Slide 19 CMOS NAND Gate A B Y 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0: Introduction ON A=1 B=0 CMOS VLSI Design OFF Y=1 ON OFF Slide 20 CMOS NAND Gate A B Y 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0: Introduction OFF A=1 B=1 CMOS VLSI Design OFF Y=0 ON ON Slide 21 CMOS NOR Gate A B Y 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0: Introduction A B Y CMOS VLSI Design Slide 22 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 23 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 Y A B C 0: Introduction CMOS VLSI Design Slide 24