* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BJT in Saturation Mode
Air traffic control radar beacon system wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
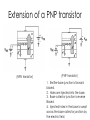
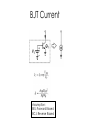
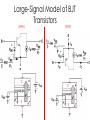
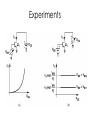
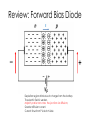
BJT in Saturation Mode Section 4.5 Outline • Modes of Operations • Review of BJT in the active Region • BJT in Saturation Mode Modes of Operation BE\BC Forward Biased Reverse Biased Forward Biased Saturation Active Reverse Biased Reverse Active Mode Cut-Off Applications: 1. Saturation and cut-off mode are used in digital circuits. 2. Active mode is used in the amplifier design. Extension of a PNP transistor (NPN transistor) (PNP transistor) 1. Emitter-base junction is forward biased. 2. Holes are injected into the base. 3. Base-collector junction is reverse Biased. 4. Injected holes in the base is swept across the base-collector junction by the electric field. BJT Current Assumption: BEJ: Forward Biased BCJ: Reverse Biased Large Signal Model of a BJT Called “large” signal model because this model is applicable even if VBE changes from 300 mV to 800 mV Large-Signal Model of BJT Transistors (NPN) C E (PNP) C E Experiments Saturation Mode BJT in Saturation Mode (A transistor in the active mode of operation) Key assumption so far: BE=Forward Biased BC=Reverse Biased What happens when these assumptions are not true? Review: Forward Bias Diode E Depletion region shrinks due to charges from the battery. The electric field is weaker. Majority carrier can cross the junction via diffusion; Greater diffusion current. Current flows from P side to N side Hole Current into the Collector A reverse biased BCJ keeps holes in the base. But as BCJ becomes forward biased, the strong electric field which opposes of the movement of holes into the collector is weakened. There is now a hole current into the collector. Net Result: heavy saturation leads to a sharp rise in the base current and a rapid fall in β. A Large Signal Model of the BJT The net collector current decreases as the collector enter into saturation General Rules • As a rule of thumb, we permit soft saturation with VBC <400 mV because the current in the B-C junction is negligible, provided that various tolerances in the component values do not drive the device into deep saturation. • For a device in soft saturation or active region, we approximate IC as Isexp(VBE/VT) • In the deep saturation region, the collector-emitter voltage approaches a constant value called VCE, SAT (about 200 mV). Voltage and Current Polarities of NPN and PNP transistors A “fat” voltage between collector and emitter voltage places a transistor in the active region! A “skinny” voltage between collector and emitter voltage places a transistor in the active region! Design Problem How do you get a transistor out of Saturation? Use 2n3904 npn BJT in Simulation (Error!, put 2n3904 here!) Include 2n3904 (NPN) model