* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download congruent angles
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
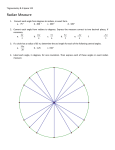
1.4: Measure and Classify Angles 1. 2. 3. 4. Objectives: To define, classify, draw, name, and measure various angles To use the Protractor and Angle Addition Postulates To construct congruent angles and angle bisectors with compass and straightedge To convert angle measurement between degrees and radians Vocabulary As a group, define each of these without your book. Draw a picture for each word and leave a bit of space for additions and revisions. Angle Vertex Sides Acute Obtuse Right Straight Congruent ’s Angle Vertex A Sides B C • An angle consists of two different rays (sides) that share a common endpoint (vertex). – Angle ABC, ABC, or B A “Rabbit Ear” antenna is a physical model of an angle Angle • An angle consists of two different rays (sides) that share a common endpoint (vertex). – Angle ABC, ABC, or B Example 1 How many angles can be seen in the diagram? Name all the angles. W Y X Z How Big is an Angle? Is the angle between the two hands of the wristwatch smaller than the angle between the hands of the large clock? – Both clocks read 9:36 Measure of an Angle The measure of an angle is the smallest amount of rotation about the vertex from one side to the other, measured in degrees. • Can be any value between 0 and 180 • Measured with a protractor Classifying Angles Surely you are familiar with all of my angular friends by now. How To Use a Protractor The measure of this angle is written: mABC 34 Example 2 Complete your Protractor Practice worksheet. 1. Write your answer in the form mABC 2. Draw your angles on the back and label them something! Example 3 What is the measure of DOZ? D G 25 O 40 Z Example 3 You basically used the Angle Addition Postulate to get the measure of the angle, where mDOG + mGOZ = mDOZ. D G 25 O 40 Z Angle Addition Postulate If P is in the interior of RST, then mRST = mRSP + mPST. Example 4 Given that mLKN = 145°, find mLKM and mMKN. M L 2x+10 4x-3 K N Congruent Angles • Two angles are congruent angles if they have the same measure. Add the appropriate markings to your picture. Congruent Angles Draw angle A on your paper. How could you copy that angle to another part of your paper using only a compass and a straightedge? Congruent Angles 1. Draw angle A. Congruent Angles 2. Draw a ray with endpoint A’. Congruent Angles 3. Put point of compass on A and draw an arc that intersects both sides of the angle. Label these points B and C. Congruent Angles 4. Put point of compass on A’ and use the compass setting from Step 3 to draw a similar arc on the ray. Label point B’ where the arc intersects the ray. Congruent Angles 5. Put point of compass on B and pencil on C. Make a small arc. Congruent Angles 6. Put point of compass on B’ and use the compass setting from Step 5 to draw an arc that intersects the arc from Step 4. Label the new point C’. Congruent Angles 7. Draw ray A’C’. Angle Bisector An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. Bisect an Angle 1. Draw an acute angle and label the vertex A. Bisect an Angle 2. Using vertex A as the center, draw an arc intersecting both sides of your angle. Label the intersections B and C. Bisect an Angle 3. Using the same compass setting, draw two intersecting arcs in the interior of your angle, one centered at B, the other centered at C. Bisect an Angle 4. Label the intersection D. Bisect an Angle 5. Draw a ray from vertex A through point D. Example 5 In the diagram, YW bisects XYZ, and mXYW = 18°. Find mXYZ. X W Y Z Example 6 In the diagram, OE bisects angle LON. Find the value of x and the measure of each angle. Radians You can also measure an angle in radians. Radians are like the less well-known greasy, nerdy-type who eats lots of pie. Radians One radian is the measure of the angle formed by stretching the radius of a circle around its circumference. Example 7 How many radians would be the equivalent to one full revolution around the unit circle? How many radians would equal 180°? Example 8 Use the conversion factor 180° = radians to convert the following angle measures. 1. Convert 27° into radians. 3 2. Convert rad into degrees. 4