* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.1 – Classifying Triangles
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
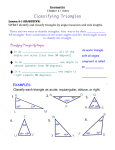
4.1 – Classifying Triangles Triangles • A polygon with three sides. • The corners are called vertices • A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is called “triangle ABC” or “ ABC Classifying Triangles by Sides Scalene Triangle No congruent sides Isosceles Triangle Equilateral Triangle 3 congruent sides 2 congruent sides Classifying Triangles by Angles Acute Triangle Obtuse Triangle All acute angles 1 obtuse angle Right Triangle Equiangular Triangle 1 right angle All congruent angles Example 1: Classify triangles by sides and angles a) b) c) 7 40° 15° 25 24 70° 70° 120° Solutions: a) Scalene, Right b) Isosceles, Acute c) Scalene, Obtuse 45° Example 2: Classify triangles by sides and angles Now you try… a) b) 5 3 5 5 4 5 c) 110° Review: The distance formula To find the distance between two points in the coordinate plane… ( x2 x1 ) ( y2 y1 ) 2 2 EXAMPLE 3 Classify a triangle in a coordinate plane Classify PQO by its sides. Then determine if the triangle is a right triangle. SOLUTION STEP 1 Use the distance formula to find the side lengths. OP = = ( x2 – x1 ) 2 + ( y2 – y1 ) 2 ( (– 1 ) – 0 ) 2 + ( 2 – 0 ) 2 = OQ = ( x2 – x1 ) 2 + ( y2 – y1 ) 2 = ( 6 – 0 )2 + ( 3 – 0 )2 = 5 2.2 45 6.7 EXAMPLE 3 Classify a triangle in a coordinate plane (continued) PQ = = ( x2 – x1 ) 2 + ( y2 – y1 ) 2 ( 6 – (– 1 )) 2 + ( 3 – 2 ) 2 = 50 7.1 STEP 2 Check for right angles by checking the slopes. There is a right angle in the triangle if any of the slopes are perpendicular. 2–0 The slope of OP is = – 2. –2–0 The slope of OQ is 3 – 0 = 1 . 2 6–0 so OP OQ and ANSWER Therefore, POQ is a right angle. PQO is a right scalene triangle. Example 4: Classify a triangle in the coordinate plane Now you try… Classify ΔABC by its sides. Then determine if the triangle is a right triangle. The vertices are A(0,0), B(3,3) and C(-3,3). Step 1: Plot the points in the coordinate plane. Example 4: (continued) Classify a triangle in the coordinate plane Step 2: Use the distance formula to find the side lengths: AB = BC = CA = Therefore, ΔABC is a ______________ triangle. Example 4: (continued) Classify a triangle in the coordinate plane Step 3: Check for right angles by checking the slopes. The slope of AB = The slope of BC = The slope of CA = Therefore, ΔABC is a ______________ triangle.