* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
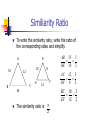
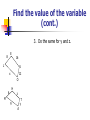
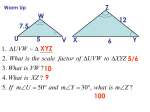
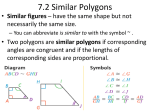
Geometry Lesson 4.3A Similarity T.2.G.1 Apply congruence (SSS …) and similarity (AA …) correspondences and properties of figures to find missing parts of geometric figures and provide logical justification M.3.G.4 Use (given similar geometric objects) proportional reasoning to solve practical problems (including scale drawings) M.3.G.5 Use properties of parallel lines and proportional reasoning to find the lengths of segments CGT.5.G.5 Draw and interpret the results of transformations and successive transformations on figures in the coordinate plane translations reflections rotations (90˚, 180˚, clockwise and counterclockwise about the origin) dilations (scale factor) Two polygons are similar if: 1. Corresponding angles are congruent 2. Corresponding sides are proportional Similarity Ratio Similarity Ratio – the ratio of the lengths of corresponding sides of similar triangles A 15 B D 10 12 C 18 E 8 12 F Similarity Ratio Corresponding angles are congruent. (Mark congruent angles) A 15 B D 10 12 C 18 E 8 12 F Similarity Ratio To write the similarity statement, keep the corresponding vertices in the same order: ABC ~ DEF A 15 B D 10 12 C 18 E 8 12 F Similiarity Ratio To write the similarity ratio, write the ratio of the corresponding sides and simplify. A 15 10 12 C B E 8 F 12 18 AB 15 3 DE 10 2 D AC 12 3 DF 8 2 BC 18 3 EF 12 2 The similarity ratio is 3 2 Find the value of the variable. Given: LOVE MATH 8 E 1. Find the similarity ratio. 16 L V x LE 8 4 MH 6 3 12 O 6 H z T M y 9 A Find the value of the variable (cont.) 8 E 16 L V x 12 O H 6 z M 9 A T y 2. Write a proportion and solve for x. Find the value of the variable (cont.) 3. Do the same for y and z. E 8 16 L V x 12 O H 6 z M 9 A T y Use the given information to solve for x (round to the nearest tenth.) Given ABC; DE || BC . A 1. Since 15 7 D DE || BC, E then B D and C E. 3 B x C 2. Therefore, ABC ~ ADE Use the given information to solve for x (round to the nearest tenth.) Continued Since ABC ~ ADE , we can write a proportion to solve for x. A 15 7 D E 3 B x C Use the given information to solve for x (round to the nearest tenth.) Given ABC; A x D 6 E 4 B 9 C DE || BC . Use the given information to solve for x (round to the nearest tenth.) a b c Given a || b || c. 10 17 x 30 •If parallel lines are cut by a traversal, the segments between the parallel lines are proportional. •We can set up a proportion to solve for x.