* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sea Level Change Concept Maps
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Sierra Madre Occidental wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
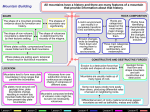
Mountain Building SHAPE All mountains have a history and there are many features of a mountain that provide information about that history. ROCK COMPOSITION The shapes of mountains vary significantly. A rock's environment can modify it or completely transform it into something else. The shape of a mountain provides evidence about its formation and history. The shape of non-volcanic mountains is determined by their tectonic setting. The shape of volcanoes is determined by the viscosity of the magma. Where plates collide, compressional forces cause folded and thrust fault mountains. Where plates are pulling apart, tensional forces result in fault block mountains. LOCATION Mountains composed entirely of volcanic rocks might be, but are not necessarily, volcanoes. Lesson 2 As plates move around over geologic time, plate boundaries change, resulting in modern day mountain belts that are far from present-day plate boundaries. Erodability is determined by a rock's resistance to mechanical and chemical weathering. Rocks have identifying characteristics that provide evidence of the changes that they have endured. Three main categories are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Geologic forces that form and shape mountains are both constructive and destructive. Mountains tend to form near plate boundaries in long ranges that parallel the boundaries. Volcanoes form over subduction zones as continuous arc-shaped chains of volcanoes of different sizes. Lesson 1 Erosion changes rocks by breaking them down and moving them to different environments. Rocks are categorized based on the most recent major change that occurred to them. CONSTRUCTIVE AND DESTRUCTIVE FORCES Erosion is a destructive force that sculpts and shapes all mountains. Mountains are usually made up of many types of rock. Some rock types erode more easily than others, producing differential rates of erosion in neighboring rocks. Differential erosion of rocky material produces jagged mountains as well as batholiths, mesas and buttes. Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Lesson 6