* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characterization of Bacteria Responsible for Background Anomalies
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Bacteriophage wikipedia , lookup
Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Escherichia coli wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
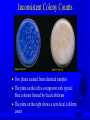
Characterization of Bacteria Responsible for Background Anomalies in the Enumeration of Fecal Coliform Bacteria by the Membrane Filter Technique Esther P. Tennant-Clegg Jerald D. Hendrix Apogee Colony Counting System Background interference caused by non-fecal coliforms interfered with both automated and manual fecal coliform enumeration. Inconsistent Colony Counts Two plates created from identical samples. The plate on the left is overgrown with typical blue colonies formed by fecal coliforms The plate on the right shows a zero fecal coliform count. Bacteria Isolated from Water Samples on mFC agar: Typical and Atypical Group Designation Identification Typical fecal coliform Escherichia coli Growth on mFC agar Inhibited by Rosolic Acid? Blue colonies Blue background No Yellow colonies Yellow background No Nonfermentative Pseudomonas maltophilia gram-negative bacillus Pseudomonas putrefaciens Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Acinetobacter lwoffi Flavobacterium odoratum Bordetella bronchiseptica Yellow colonies Yellow background No Atypical: gramGram-positive streptococcus positive streptococcus Blue colonies Blue background No A lactosenonfermenting variety Escherichia fergunsonii of Escherichia Standard Membrane Filter Technique 0.45 mm nitrocellulose filter mFC Agar Rosolic acid to inhibit background interference Incubation at 44.5°C ± 0.5°C for 24 hrs in water bath Plates are incubated in a watertight bag or box The Effect of Selected Bacteria on Agar Surface pH 9 8.5 Final Surface pH (Initial pH = 7.5) 8 7.5 7 6.5 6 5.5 5 4.5 Escherichia coli Pseudomonas maltophila Pseudomonas putrefaciens Acinetobacter lwoffi Common Features of Atypical Bacteria on mFC Produce higher pH (up to 8.5) in the mFC Agar Agar turns transparent yellow Aerobic Non-fermentative Not inhibited by rosolic acid Methods Used to Identify Bacteria Gram Stain Wet mount slide to observe motility Catalase and Oxidase Test SIMS Agar to discover Indole reactions, and Oxygen requirements Fermentation Tubes (Sucrose, Lactose, Glucose) Oxiferm and Enterotube rapid biochemical test (Beckton Dickinson) Limited Oxygen Incubation Method Agar is poured close to the top lip of plate limiting the area between bacterial growth and lid. Each plate is individually wrapped with parafilm prior to incubation. All other aspects of the Standard Method of Membrane Filter Technique remain unchanged. Effect Of Limited 02 on Background and Growth of E. coli Atmospheric O2 Levels Limited O2 Levels Effect Of Limited 02 on Background and Growth of Atypical Isolates Atmospheric O2 Levels Limited O2 Levels ph ila ut rif A ac .c ie al ns co ac et ic us A .l w of F. fi od B. or at br um on ch is ep tic a Ps .p al to i ii co l ns on E. fe rg u Ps .m E. Final Surface pH (Initial pH = 7.5) Growth of Bacteria in Aerobic and Limited O2 Conditions: Effect on Agar Surface pH 9 8.5 8 7.5 7 6.5 Aerobic Limited O2 6 5.5 5 4.5