* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download m5zn_50ef57ae8899445
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
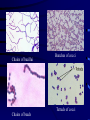
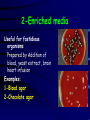
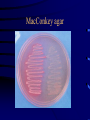
MICROSCOPES Microscopes Microscope : an instruments used to examine very small objects (Specimens) in microbiology. Functions : To allow us to study the morphology of bacteria (size, shape, arrangement, motility and staining reaction ) Types of microscopes 1-light microscope 2-Dark field microscope 3-fluorescent microscope 4-Phase contrast microscope 5-Electron microscope • Light Microscope • • • • • • • Eye piece Objective lenses Stage Diaphragm Condenser Light source Adjustment knobs STAINING METHODS Types of stain 1-Simple stain (one dye is used ) Methylene blue, safranin, crystal violet. 2-differential stains( two dyes are used) Gram stain ,Ziehl-Neelsen stain. 3-special stains fontana stain. 4- Fluorescent stained antibody Antibodies for surface antigens of bacteria carrying a fluorescent dye Simple stains 1- preparation of smear: • Take a loopfull of bacterial suspension and spread it onto an area of about 1 cm square • Leave to dry in air or at the warmth of a Bunzen flame • Fix the smear by: a- passing it into a flame three times b- dipping into ethyl alcohol Fixation leads to coagulation of proteins and fixation on the surface of slide. Simple stains 2-staining of the smear: a- Flood the smear with several drops of a stain like methylene blue and leave for 2 min. b- wash the stain gently with water c- Dry the smear by leaving it in air for a few minutes or by blotting with a filter paper. Simple stains 3- Examination under the microscope • Put a drop of oil onto the stained smear • Examine the smear under the oil immersion lens • Describe what you can see under the microscope Chains of bacillui Chains of beads Bunches of cocci Tetrads of cocci Gram-stain • Principles: • Bacteria differ from one another chemically and physically and may react differently to stains. • Bacteria are divided into 1- Gram-positive bacteria (violet in colour) 2- And Gram-negative bacteria (red in colour) Gram-stain:Steps of staining: • 1- Prepare a bacterial smear and fix it • 2- Flood with crystal violet (primary stain) and leave 60 sec. Wash gently with tap water. • 3- flood with iodine solution (mordant) and leave for 2 min and then wash gently with tap water. Gram-stain:Steps of staining: 4-Declourize with drop by drop 95% ethanol alcohol (decolourization of Gram-negative bacteria), till the washing becomes faint purple (this takes about 20 sec). Wash gently with water. 5- Flood the smear with safranin (counter stain) and leave for 2 min. 6- Dry the smear by blotting, add a drop of oil and examine under oil immersion lens Technique of isolation of separate colonies of bacteria Technique for isolates • Sterilize the loop by heating to redness on the top of a flame. • Take one loop-full of bacteria and streak the surface of nutrient agar plate to spread bacteria in area [1] as indicated in the photo. • Sterlilize the loop and make other streaks starting from the side of area [1] as shown in the photo to spread bacteria in area [2]. • Repeat the same procedure to spread bacteria in area [3]. Colonies isolated Types of media : Types of media : 1-basal media 2-Enriched media 3-Selective media 4- Enrichment media 5-Differential media 6- selective and indicator media 1-Basal media 1- Nutrient broth 2-Peptone water (Water soluble products obtained from protein materials digested by proteolytic enzyme as trypsin and pepsin). 3- Nutrient agar 4-Nutrient gelatin nutrient agar 2-Enriched media Useful for fastidious organisms Prepared by Addition of blood, yeast extract, brain heart infusion Examples: 1-Blood agar 2-Chocolate agar 3-Selective media Contain substances that inhibit the growth of some organism but have no effect on the organism of test .these inhibitors may be dyes ,chemicals or antibiotics. An example is Mannitol salt agar used to separate staphylococcus aureus Mannitol salt agar Staphylococcus aureus produce yellow colouration 4- Enrichment media These are liquid media with selective properties enhance the multiplication of organisms. As: 1-Selenite broth. 2-Alkaline peptone water 3-Tetrathionate broth medium 5-Differential media Contain some substances that are changed visibly as a result of metabolic activity of organism as: 1-Sugar media 2-Triple sugar iron agar (TSI) 6- Selective and indicator media . Composed of selective and indicator supplements in basal media as: 1- MacConkey’s agar 2-Deoxycholate citrate agar (DCA). 3-TCBS(Thiosulphate citrate and bile salt (selective) sucrose (test sugar) and bromothymol blue (pH indicator) MacConkey agar