* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gram staining
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
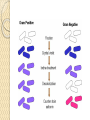
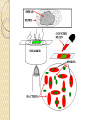
Differential staining Lab 7 Abeer Saati Differential staining Gram staining It is based on the composition of their cell wall. Gram staining uses crystal violet to stain cell walls, iodine as a mordant, and a fuchsin or safranin counterstain to mark all bacteria. Gram status is important in medicine; the presence or absence of a cell wall changes the bacterium's susceptibility to some antibiotics. Gram-positive bacteria stain dark blue or violet. Their cell wall is typically rich with peptidoglycan and lacks the secondary membrane and lipopolysaccharide layer found in Gram-negative bacteria (red). Gram staining 1-Preparation of smears 2-Fixation of smears 3-Staining of smears • • • • • • • • • Cover the smear with crystal violet for 1 minute. Pour it off then wash with water. Add iodine solution to the smear for 1 minute. Gently wash with water. Decolorize by 95% alcohol and rock the slide from side to side and pour it off. Reapply alcohol till no violet color comes off. Wash with water Counterstain with safranin for 1 min. Wash with water. Place the film at angle to air dry or dry with filter paper. Gram staining 1- Preparation of smears: o Put a drop of water on the middle of the slide using the inoculating needle. o With the sterile needle, collect bacteria from agar surface by touching the bacterial growth. o Rub the tip of the needle on the glass slide in the drop of water in a circular motion till you get homogenous smear. o Allow the smear to dry. Gram staining 4-Examination of smears Spore staining Spore: structure that can survive for long periods of time in inert state. Produced when environmental conditions are poor. Do not stain well with simple stains required (heat) • Prepare a smear of the bacteria • Flood the smear with malachite green • Do not allow the stain to completely evaporate. • Remove from heat and allow slides to cool • Once the slides are cool (important) rinse with water • Flood the sample with safranin (30-60 seconds) • Rinse the slide blot dry observe under microscopy. 10x, 40x, 100x (oil immersion). • Spore: (green) • Vegetative cell: (red) Thank You