* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download .NET Framework Overview and Base Classes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
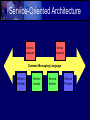
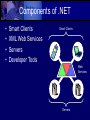
Creating Business Value with .NET Drew Robbins InDepth Technology Overview • Service-Oriented Architecture • Overview of .NET Technology • XML Web Services Software Architecture • High-Level Structures of Software • Components of System • Interactions between Components Architecture Patterns • • • • • Mainframe File Sharing Client/Server Three Tier and N-Tier REpresentational State Transfer (REST) Architecture Soup DCOM COBOL Service-Oriented Architecture • Wrap Application Components in WellDefined Interfaces • Common Messaging Language • Flexibility on how to Implement Interface • Flexibility on how to Consume Interface Service-Oriented Architecture Service Requestor Service Requestor Common Messaging Language Service Provider Service Locator Service Broker Service Provider .NET Defined • Group of Microsoft software technologies. • Connects information, systems and devices and the people that use them. • Build on Industry Standards for secure communication. Components of .NET • • • • Smart Clients XML Web Services Servers Developer Tools Smart Clients Web Services Servers .NET Framework • • • • • Improved Developer Productivity Better Deployment Mechanisms Interoperability and Management Increased Security Rich Device Support .NET Framework Components Managed Windows Applications Managed Web Applications Custom Class Libraries Framework Class Library Common Language Runtime ASP.NET (Runtime) App.exe Library.dll IIS Operating System Common Language Runtime • • • • • • Manages Memory Code/Thread Execution Code Safety Verification Just-in-Time Compilation Type Verification Garbage Collection Common Type System • Specification for common way to define types. – Field, Method, Property, Event • Type Visibility – Public, Private, Family, Assembly, Family and Assembly, Family or Assembly • This allows all languages to target the CLR by compiling to a common Intermediate Language base on the CTS. Application Types • • • • • • Console Applications Scripted/Hosted Applications Windows GUI Applications ASP.NET Applications Windows Services XML Web Services XML Web Services • Loose Coupled, Service-Oriented • XML as Common Interface Language • Web Services Definition Language (WSDL) • Universal Description, Discovery, Integration (UDDI) • Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) XML Web Services Rich Client Application Other Service Component XML/SOAP WSDL Purchase Order System Service Locator Service Broker UDDI WS-Referral Enterprise Resource Mgmt Example Web Service I • Research Pane in Office 11 – Implement WSDL defined by MS – Factiva, WorldLingo Services – Build your own • Example of Google Research Website Integrated Search Office 11 Research XML/SOAP Research WSDL Google Web Service Service Locator Service Broker UDDI WS-Referral Google Research Service Example Web Service II • Amazon.com Exposes Web Service – Use SOAP or XML over HTTP (REST) – Display Product Lists – Enable Searches – Integrate with Shopping Cart – Amazon Associates Program Example Web Service III • Using InfoPath to submit information to a web service – BERT – Bug and Enhancement Request Tracking – Submission service for submitting from the field – Service created before considering InfoPath Benefits of .NET Web Services • Visual Studio.NET – Developer Productivity • Built-in Caching • Automatic WSDL Generation • .NET Framework • Cross-language Compatibility Summary • .NET is a group of software technologies. • .NET Framework is a programming model. • XML Web Services are a key architectural component of .NET. • Service Oriented Architectures enable you to leverage existing applications to build flexible solutions that have business value. Questions Drew Robbins InDepth Technology [email protected]