* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theory of Markets
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
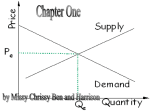
AAEC 2305 Fundamentals of Ag Economics Chapter 5 Theory of Markets Objectives: To learn: How Supply & Demand curves interact to determine the prices & quantities of goods & services produced & consumed About markets in time, space, & form Characteristics of a competitive market Determination of Output in a competitive market Market Supply In chapter 4, we discussed that the individual firm’s supply curve was the firms MC curve above AVC The total offered by all firms in the market is the aggregate or market supply. Market Supply Market Supply - is the various amounts of a good that producers are willing & able to produce and make available at each of a series of prices during a specified period in a given market. Supply curve for a good in the market is the horizontal sum of all individual firm’s supply curves. Market Demand In chapter 2, we derived the demand curve for an individual consumer that will maximize their utility based upon their preferences and budget constraint. In other words, we indicated how the consumer, with a limited budget, makes choices among available goods to maximize utility. Market Demand As with Supply, the aggregate or market demand is obtained by the horizontal summation of all individual consumer’s demand curves. Market Demand - a schedule showing the amounts of a good consumers are willing and able to purchase in the market for a series of prices during a specified period in a given market. Markets A Market is an institution or an arrangement that brings buyers and sellers together. Market Price - is the mutually agreeable price at which willing buyers and willing sellers exchange a good. Market Equilibrium Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good offered by a sellers at a given price equals the quantity buyers are willing and able to purchase at that same price.