* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Markets Operate
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
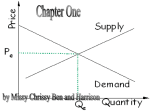
Today’s Warm Up Due to scarcity, resources are limited. We can’t all have whatever we want, whenever we want. How does a country like the U.S. decide who is going to get what? Markets Today’s LEQ: How do markets operate? Important vocabulary: Demand, Market, Equilibrium, Shortage, Supply, Surplus Economic Systems Economic systems address scarcity What, how, and for whom to produce? U.S. = mixed market economy Producers/Consumers (& limited gov’t) answer these questions Markets The market is the most important economic institution in a market economy Markets exist when buyers and sellers interact This interaction determines prices & therefore allocates scarce goods and services Market Incentives Prices send signals and provide incentives to buyers and sellers What would happen if the price of the average flat screen TV jumped to $30,000? When supply or demand changes, market prices adjust, affecting incentives For example, think of gas prices around peak vacation times! Graphing Supply Law of Supply: When price increases (decreases), the quantity supplied increases (decreases) Graphing Demand Law of Demand: When price increases (decreases), quantity demanded decreases (increases) Equilibrium Price (Market Clearing Price) The market settles at this price and quantity QS = QD Why? At this point of intersection, buyers and sellers agree on both price and quantity Surplus If price is above the equilibrium price, sellers would want to sell more than buyers would want to buy QS > QD Shortage If price is below the equilibrium price, buyers would want to buy more than sellers would want to sell QD > QS Game Time: A Market In Wheat 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. At what price was wheat most frequently sold in each round? This price is known as the market clearing or equilibrium price. Why would economists call it the market-clearing price? Why did prices become more clustered together in later rounds? Did buyers or sellers determine the price for wheat? How did competition among the sellers and the buyers influence the price? What would happen if there were many more buyers than sellers? What would happen if there were more sellers than buyers? Activity 7.5 What is the equilibrium price? What prices would result in a surplus? What prices would result in a shortage? Today’s Exit Ticket Answer today’s LEQ on the back of Activity 7.5. Be sure to use all of the key vocabulary listed below: Demand, Market, Equilibrium, Shortage, Supply, Surplus