* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
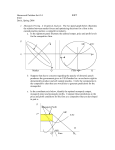
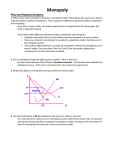
Chapter 8 Imperfect Competition © 2001 South-Western College Publishing Monopoly A market structure in which only one producer or seller exists for a product that has no close substitutes 2 Characteristics of Monopoly Degree of control over price that is held by the monopolist Individual supply of the monopolist coincides with the market supply Market demand equals the demand for the product/service Monopolist is a “price maker” 3 Sources of Monopoly Economies of Scale Natural Monopolies: Public Utilities Control of Raw Materials Patents Competitive Tactics 4 Determining Monopoly Price Monopolist’s demand curve slopes downward to the right because it is the market demand curve of all consumers Relationships between the monopolist’s cost and revenue curves 5 Monopolist’s Demand Curve Price $12 10 8 D 0 900 1,000 1,100 Units 6 Price Cost and Cost and Revenue Curves for a Monopoly $20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ATC MC B B P Pure Profit C AR A Q 10 11 1 12 2 3 13 4 5 MR 6 7 8Quant 9 ity 7 Monopolistic Competition Market structure in which relatively many firms supply a similar but differentiated product, with each firm having a limited degree of control over price 8 Product Differentiation Establishment of real or imagined characteristics that identify a firm’s product as being unique Vs. 9 Substitution Effect Change in quantity demanded of a good due to change in price relative to substitute goods Increased sales at the expense of other firms 10 Short-Run Cost and Revenue Curves: Possible Equilibrium under Monopolistic Competition (a) (c) (b) $ $ MC $ MC S ATC ATC AR AR D MR 0 0 Quant 30,000 ity Industry Quant ity Short-Run Economic Profit MR 0 28,000 Quant ity Long Run 11 Oligopoly Market structure in which relatively few firms produce identical or similar products 12 Possible Demand Curves for an Oligopolist Price D1 D P P D D1 Q Quant ity 13 Administered Price A predetermined price set by the seller, rather than a price solely determined by demand and supply in the marketplace 14 Cartel An organization of independent firms that agree to operate as a shared monopoly by limiting production and charging the monopoly price 15 Three-Firm Cartel Price P Firms 2+3 Market Share Firm 1 Market Share MC1 Dc MR1 q1 d1 Qc Quant ity 16 Measurements of Concentration Concentration Ratio: Measure of market power calculated by determining the percentage of industry output accounted for by the largest firms Herfindahl Index: Measure of market power calculated by summing the squares of the market shares of each firm in the industry 17 Perfectly Competitive vs. Monopolistic Pricing: Possible Long-Run Price Under Price Cost and Monopolistic Competition MC AC A P C P D´(MR´ and AR´) B AR MR 0 Q Q Quant ity 18 Possible Equilibriums under Perfect Competition and Monopoly or Oligopoly $ MC $ MC ATC ATC AR and MR AR MR 0 100,000 Perfect Competition Q 0 500,000 Q Monopoly or Oligopoly 19 Competition Among Consumers Monopsony: Market structure in which there is a single buyer – ex., rural area granary Oligopsony: Market structure in which there are only a few buyers – ex., commercial jet aircraft Monopsonistic Competition: Market structure in which there are many buyers offering differentiated conditions to sellers – ex., toy manufacturers 20 Market Structure in the U. S. Bilateral Monopoly: Market structure where only a single buyer exists on one side of a market, and only one seller (the monopolist) exists on the other side 21 Antitrust Laws Sherman Antitrust Act - outlaws restraint of trade and any attempt to monopolize Clayton Act - outlaws certain business activities not covered by Sherman Act Federal Trade Commission Act created the FTC to police unfair business practices 22 Activities Prohibited by the Clayton Act Price Discrimination – charging different customers different prices for the same good Tying Contracts – contracts requiring the buyer of a good to purchase another additional good Exclusive Dealing – requiring buyers of goods to agree not to purchase from competing sellers Interlocking Directorates – boards of directors of competing firms with one or more members in common Predatory Pricing – selling at unreasonably low prices to destroy competition 23