* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply & Demand
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
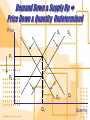
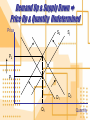
Supply & Demand Before We Start • Economic Terms: • • • • • • • • Market Competitive Market Perfectly Competitive Normal Good Inferior Good Substitutes Complements Ceteris Paribus • “Other things being equal” Demand • Quantity DemandedShift along Demand Curve • Price • Determinants of DemandShift of the Demand Curve • • • • • Price of related goods Income Tastes Expectations Number of buyers or sellers Demand Schedule • Ice cream cones • Price • • • • • • • $0.00 $0.50 $1.00 $1.50 $2.00 $2.50 $3.00 Quantity 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Demand Curve P 3 2.5 2 Demand Curve 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Q Market Demand • Market = Sum of parts • 2 person Market • Price • • • • $0.00 $1.00 $2.00 $3.00 Anne Bill Market 12 8 4 0 7 5 3 1 19 13 7 1 Shift In Demand • What happens when there is a Change in Demand? • Changes caused by factors other than price. • Examples: • > income increases demand for luxury cars • < price in gas decreases demand for economy cars Shift In Demand Question • Give two economic ways (in terms of demand) that the government could use to stop teenage smoking. • Use graphs to show your work for both answers. Supply What Determines Supply? • Determinants • Terms • Price • Law of Supply • Input Prices • Supply Schedule • Technology • Supply Curve • Expectations Supply • Quantity SuppliedMovement along Demand Curve • Price • Determinants of SupplyChange in the Demand Curve • • • • • Price of related goods Input Prices Technology Expectations Number of buyers or sellers Supply Schedule • Price • • • • • • • $0.00 $0.50 $1.00 $1.50 $2.00 $2.50 $3.00 • Quantity • • • • • • • 0 0 0 0 4 8 12 Supply Curve P 3 2.5 2 Supply Curve 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Q Shift In Supply Question • Using a supply curve graph, demonstrate the effects of the following on Health Care supply. • Universal coverage • Elimination of Caps Equilibrium • Supply & Demand • Intersection determines • Price • Quantity • Terms • Surplus • Quantity > demand • Shortage • Demand > quantity Equilibrium Graph P 3 2.5 2 Demand Curve Supply Curve 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Q In an attempt to get rid of surplus stock, producers will accept lower prices. Lower prices in tn attract some consumers to buy. S The process continues until the surplus disappears and equilibrium is once again reached. The Market - Surplus Price (£) Surplus £5 £3 D1 300 450 600 A shift in the demand curve to the left will reduce the demand to 300 from 500 at a price of £5. Suppliers do not have the information or time to adjust supply immediately and still offer 600 for sale at £5. This results in a market surplus (S > D D) Quantity Bought and Sold (000s) The shortage in the market would drive up prices as some consumers are prepared to pay more. The price will continue to rise until S the shortage has been competed away and a new equilibrium position has been reached. The Market - Shortage S1 Price (£) £8 £5 A shift in the supply curve to the left would lead to less products being available for sale at every price. Suppliers would only be able to offer 100 units for sale at a price of £5 but consumers still desire to purchase 600. This creates a market D shortage. (S < D) Shortage 100 350 600 Quantity Bought and Sold (000s) Increase in Demand Price D1 D2 Quantity Decrease in Demand Price D2 D1 Quantity Increase in Supply Price S1 S2 Quantity Decrease in Supply Price S2 S1 Quantity Demand Up & Supply Up Price Undetermined & Quantity Up Price S1 S2 D1 D2 P1 Q1 Q2 Quantity Demand Down & Supply Down Price Undetermined & Quantity Down Price S2 S1 D2 D1 P1 Q2 Q1 Quantity Demand Down & Supply Up Price Down & Quantity Undetermined Price S1 S2 D2 D1 P1 P2 Q1 Quantity Demand Up & Supply Down Price Up & Quantity Undetermined Price S2 S1 D1 D2 P2 P1 Q1 Quantity